
IP address Classes Introduction and Explanation » NetworkUstad
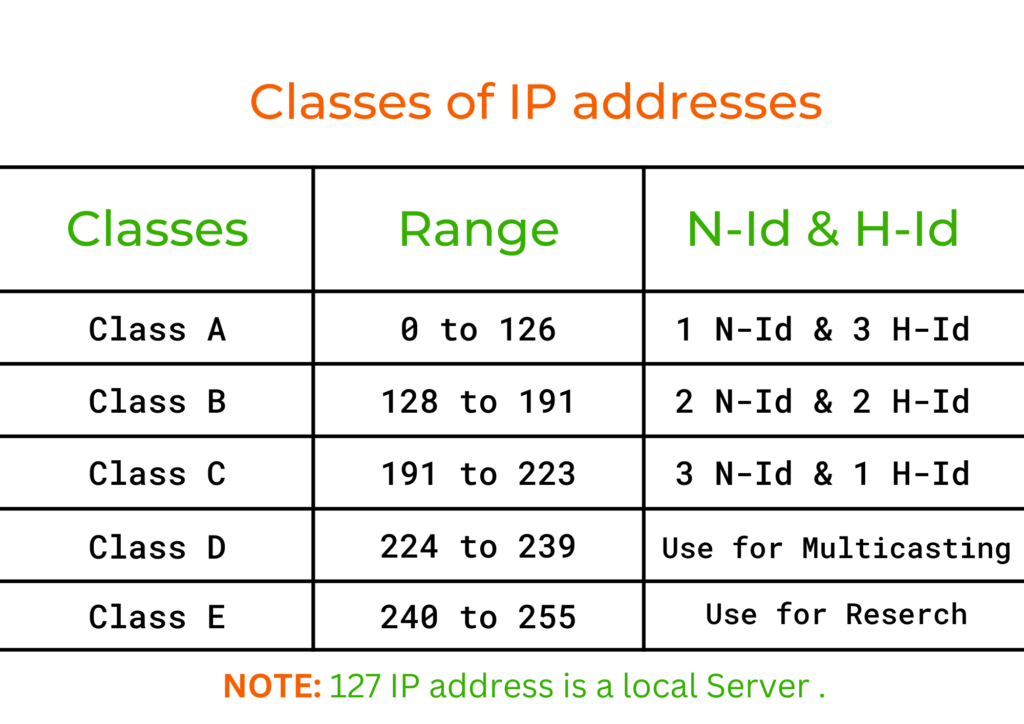
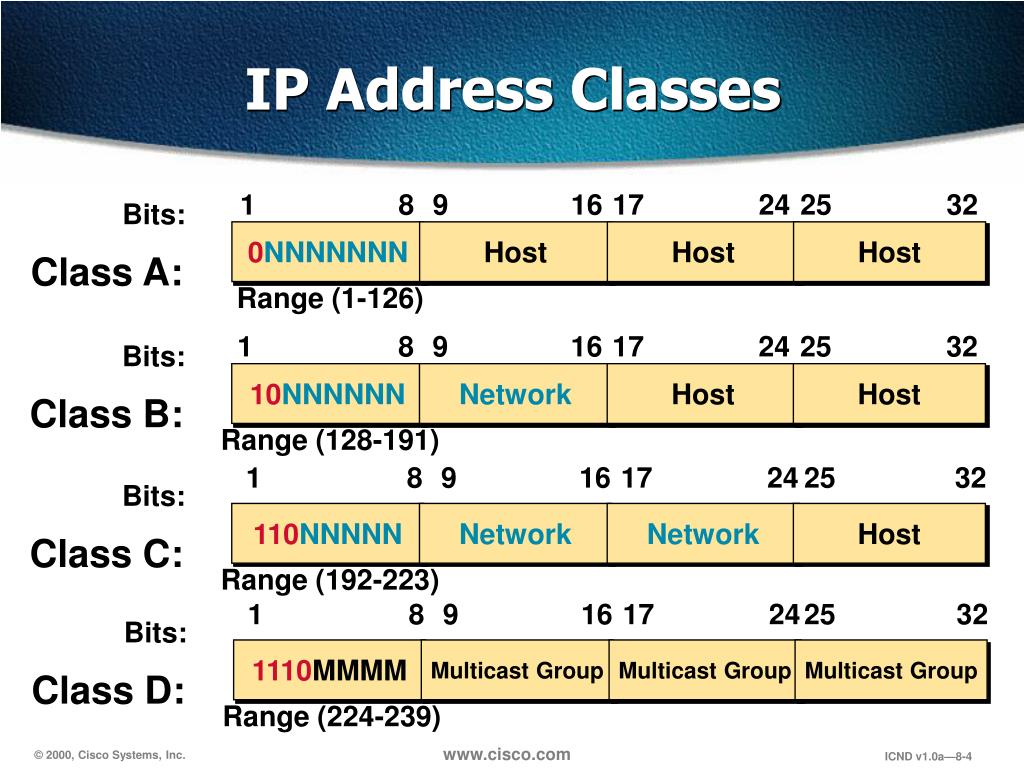
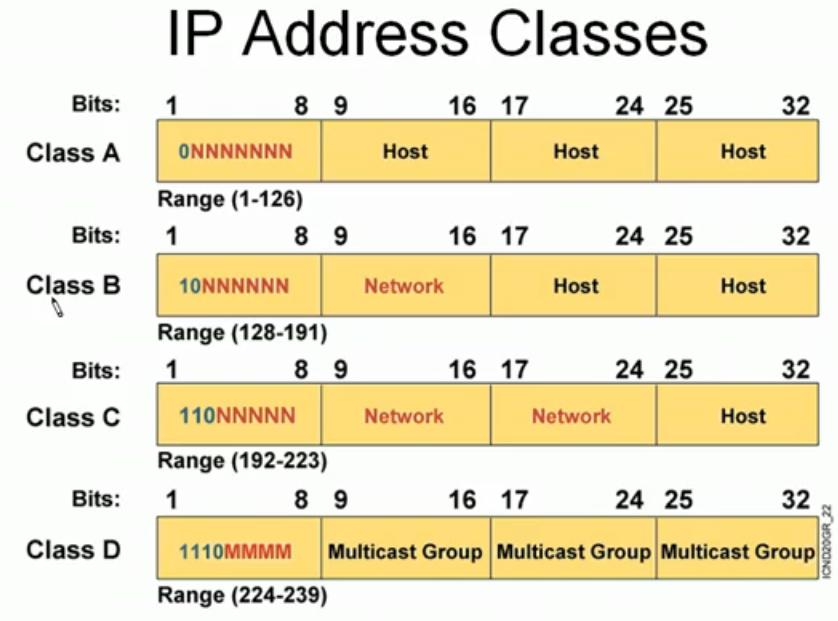
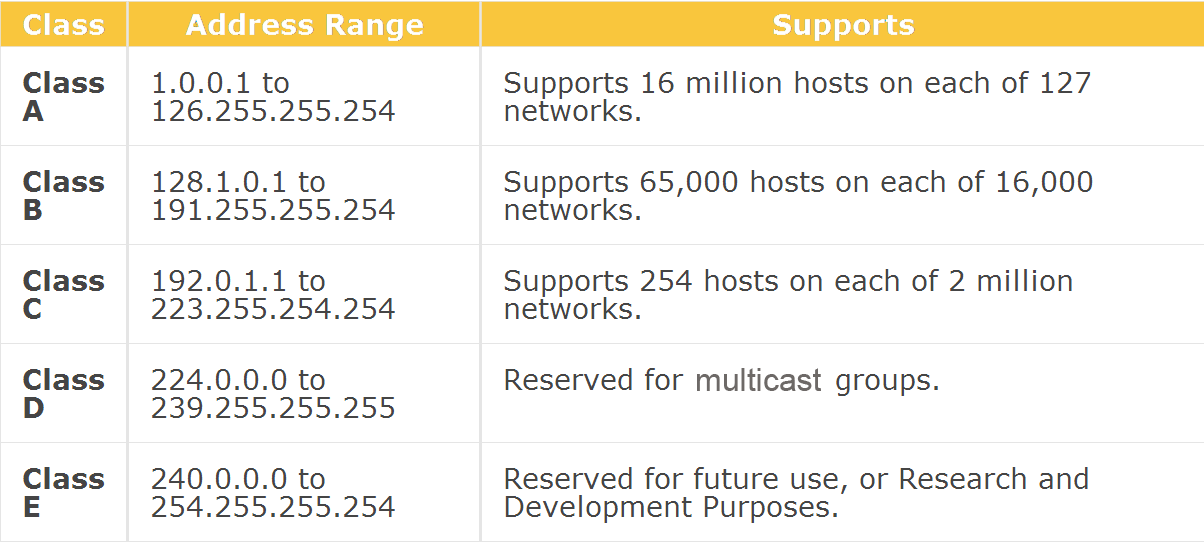
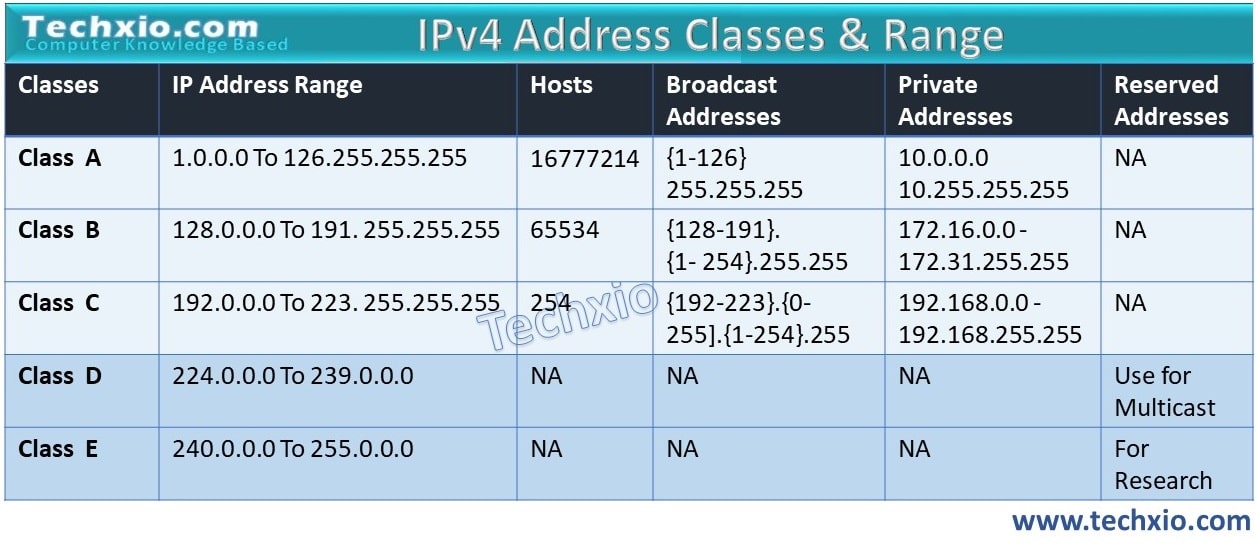
The address range of Class C falls between 192 and 223. For public IP addresses, the range spans from 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255. The private IP range lies from 192.168.. to 192.168.255.255. This is an example of an IPv4 Class C address: 198.215.7.21. Class C offers a total of 2,097,152 networks, each accommodating 256 addresses.

Classes of IP Address Class A, B, C, D and E YouTube
#IPAddressClasses #IPClassesIn this video, we have explained the different classes of IP Addresses and a very important TIP on how to remember them. Under cl.

IP Addressing Introduction and Classful Addressing
IP Address Class D and Multicast The IPv4 networking standard defines Class D addresses as reserved for multicast. Multicast is a mechanism in Internet Protocol for defining groups of client devices and sending messages only to that group rather than to every device on the LAN (broadcast) or just one other node (unicast).
Explain IP address and its classes in detail
Class E IP address is defined by including the starting four network address bits as 1, which allows you two to incorporate addresses from 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. However, E class is reserved, and its usage is never defined. Therefore, many network implementations discard these addresses as undefined or illegal.

Class of IP address in English YouTube
Class A. IP addresses belonging to class A are assigned to the networks that contain a large number of hosts. The network ID is 8 bits long. The host ID is 24 bits long. The higher-order bit of the first octet in class A is always set to 0. The remaining 7 bits in the first octet are used to determine network ID.
PPT IP Address PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3649936
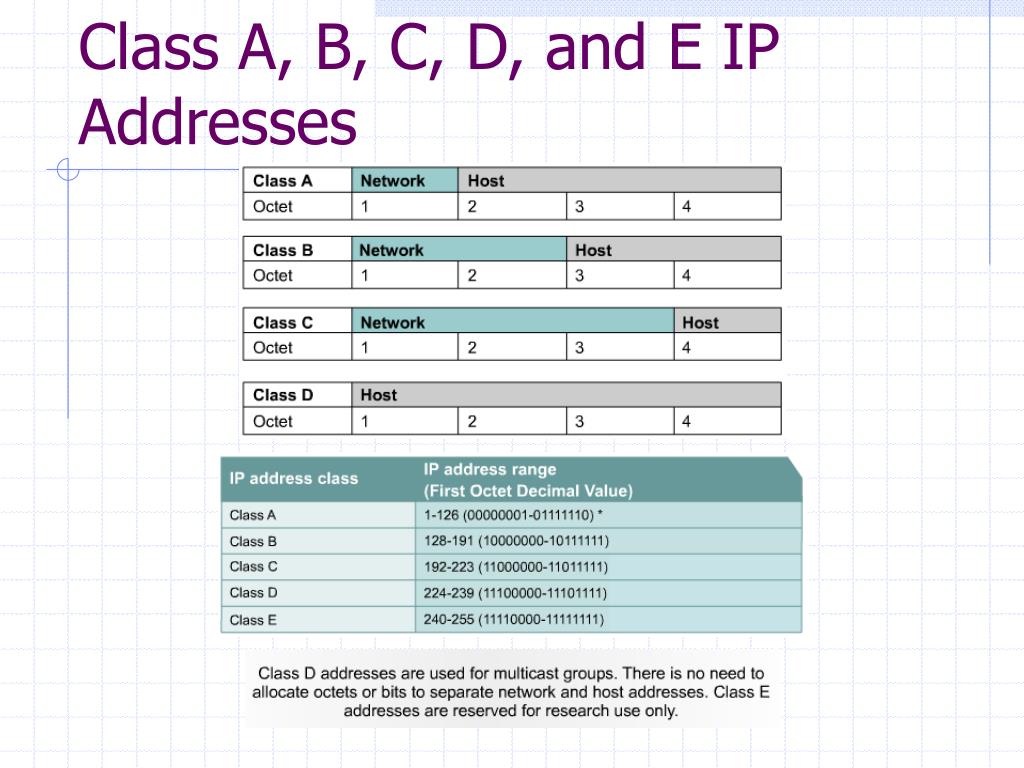
The method divides the IP address space for Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) into five address classes based on the leading four address bits. Classes A, B, and C provide unicast addresses for networks of three different network sizes. Class D is for multicast networking and the class E address range is reserved for future or experimental.
Comptia Network+ Tutorial Module 01, Part 03 IP Addressing
IPv4 address class: An IPv4 address class is a categorical division of internet protocol addresses in IPv4-based routing.

IP address Classes Introduction and Explanation » NetworkUstad
Class B. Class B IP address always has its first bits as 10, next 14 bits as a network address and following 16 bits as the host address. The range of IP addresses is 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255. This means that it allows 2^14 networks and 2^16 hosts per network. This class of IP address is used for a medium network like multinational companies.
PPT CCNA 1 v3.0 Module 9 TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP Addressing PowerPoint Presentation ID
B, C, D (Multicast), and E (Reserved). Address classes are defined, in part, based on the number of bits that make up the network portion of the address, and in turn, on how many are left for the definition of individual host addresses. • In Class A addresses, the first octet is the network portion. • In Class B, the first two octets are.
What is my IP, What is IP Adress?
The remaining 29 bits of entire 32-bit addresses can be changed to define the address space of class C i.e. 2 29 = 536,870,912. Class D. Like class A, B & C, class D does not divide IPv4 into net-id and host-id. All the addresses of class D are of one single block. The class D addresses are designed for multicasting.
Ip address classes tutorial Computer Science Junction
IP addressing classes explained. Address classes and IPv4 addressing.World-class IT certification video training, follow-along labs, practice exams and live.

IP address classes explained class A , B ,C ,D ,E Free CCNA 200301 YouTube
Class C Public & Private IP Address Range. Class C addresses are used in small local area networks (LANs). Class C allows for approximately 2 million networks by using the first three octets for the network ID. In a class C IP address, the first three bits of the first octet are always 1 1 0.

IP Address classes IP Address class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E Range
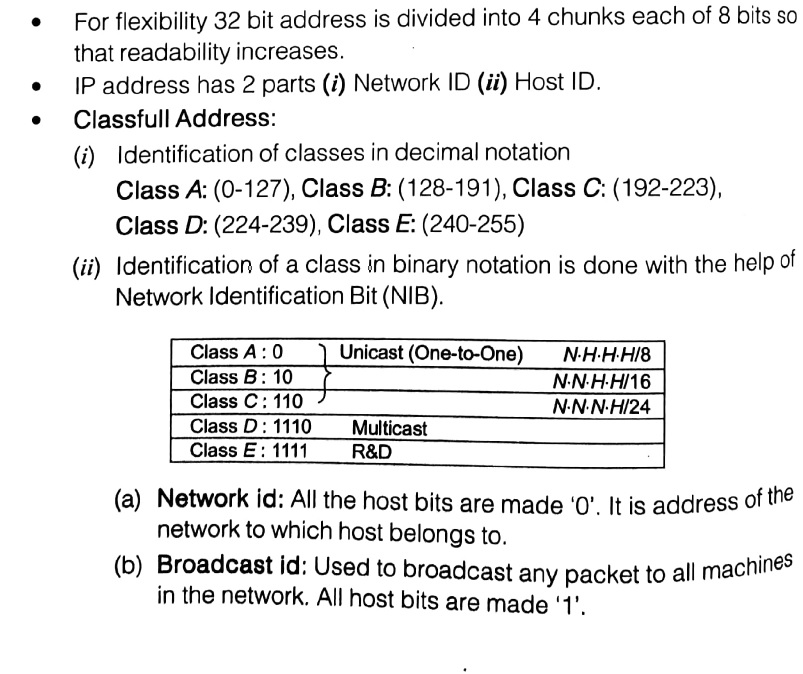
If the value is in the range 128 to 191, the address belongs to class B. If the value is in the range 192 to 223, the address belongs to class C. If the value is in the range 224 to 239, the address belongs to class D. If the value is in the range 240 to 255, the address belongs to class E. Identifying the class of an IP address (binary notation)
IPv4 Address Classes and Range
A Subnet Mask is a numerical value that describes a computer or device's how to divide an IP address into two parts:. (Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, Class E) of fixed length. In Classful addressing IP addresses are allocated according to the classes- A to E. In this Scheme, Network ID and Host ID changes depend on the class.
IP Addressing Classes
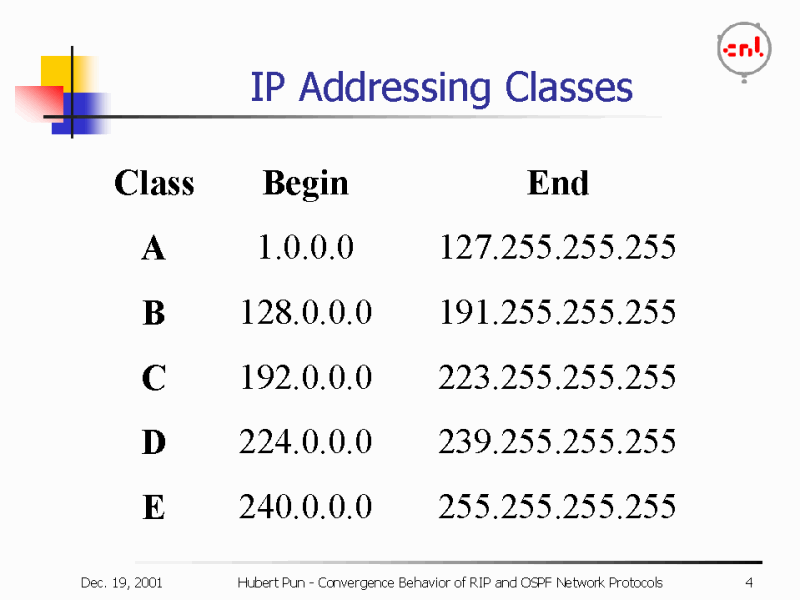
Class A IP address has the first octet starting from 0, class B starts from 0+128 = 128.. Class C ends at 223, Class D at 239, and Class E at 255. First Octet in Decimal.

PPT Lecture 1 IP V.4 Addressing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2061405
Each class has a range of valid IP addresses. The value of the first octet determines the class. IP addresses from the first three classes (A, B and C) can be used for host addresses. The other two classes are used for other purposes - class D for multicast and class E for experimental purposes. The system of IP address classes was developed.