My Classroom Blog Meiosis
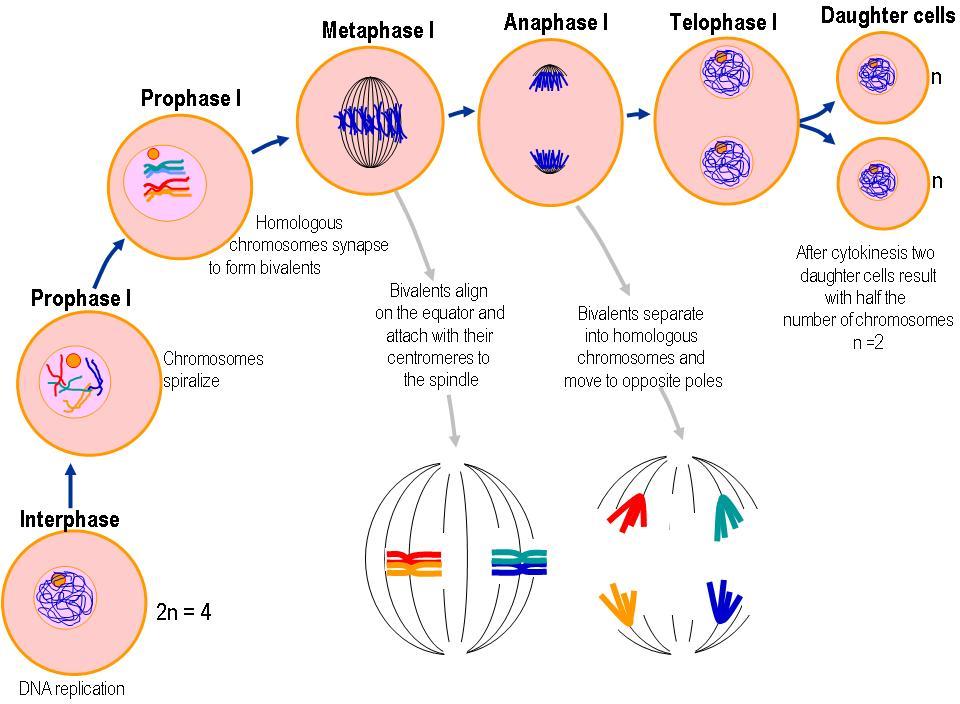
Meiosis 2 results in separation the sister chromatids and for this reason, it is known as equatorial division. Each of the two meiotic divisions is divided into interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Each stage is followed by 1 or 2 indicating whether it belongs to meiosis 1 or 2. Here are list of stages of meiosis 1 and.
Qué es la Meiosis y cuales son las fases de la Meiosis.
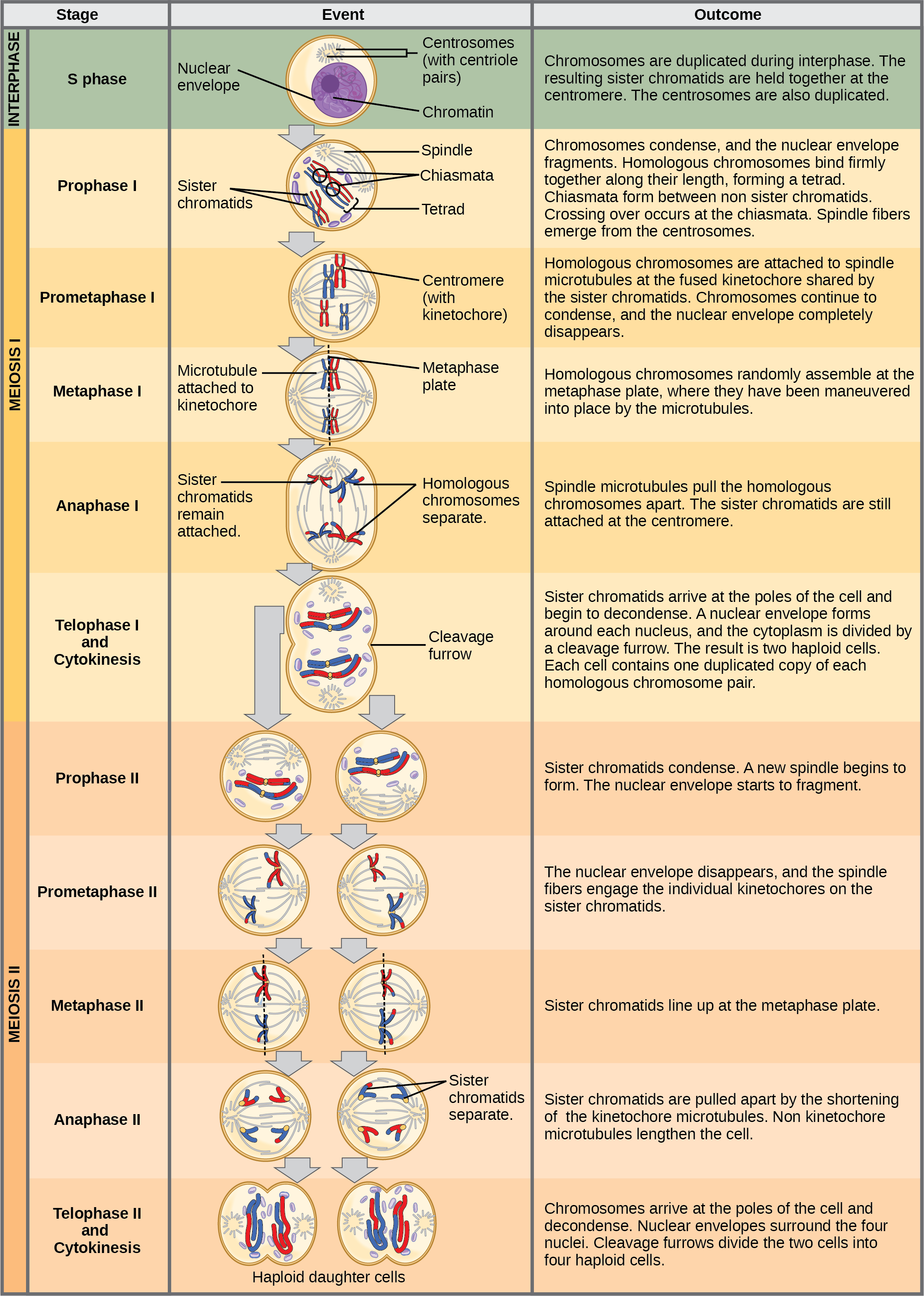
Meiosis I takes place, and there are 2 cells, each with only 4 chromosomes. Each chromosome is still made of sister chromatids, and some crossing-over may have occurred during metaphase I. Meiosis II now takes place on those two cells. In total, 4 cells are created, again. However, these cells have 4 chromosomes.

Cómo explicar las fases de la meiosis a los niños Eres Mamá
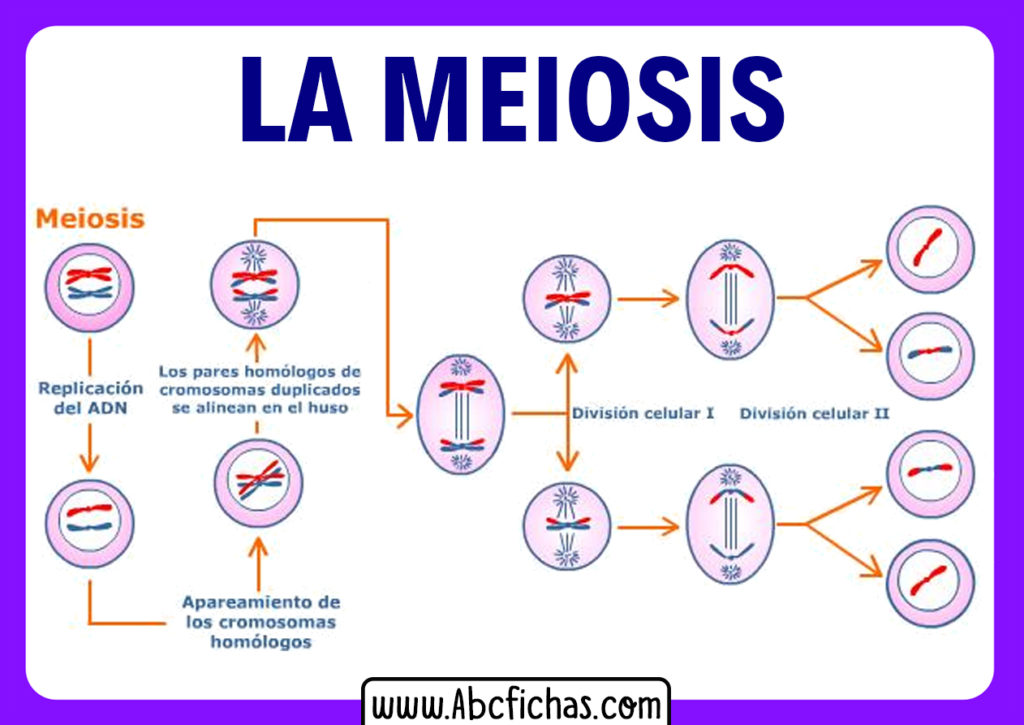
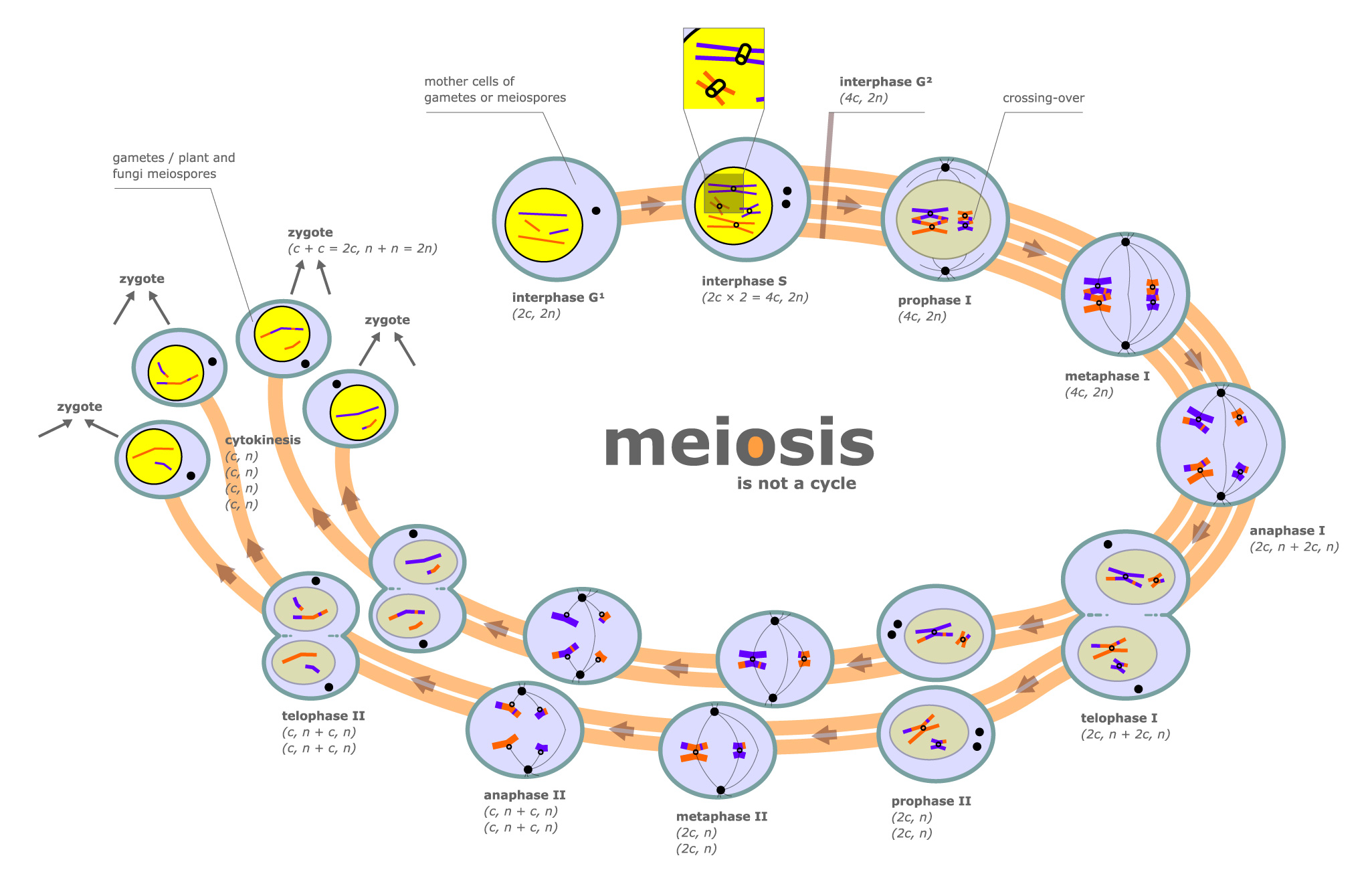
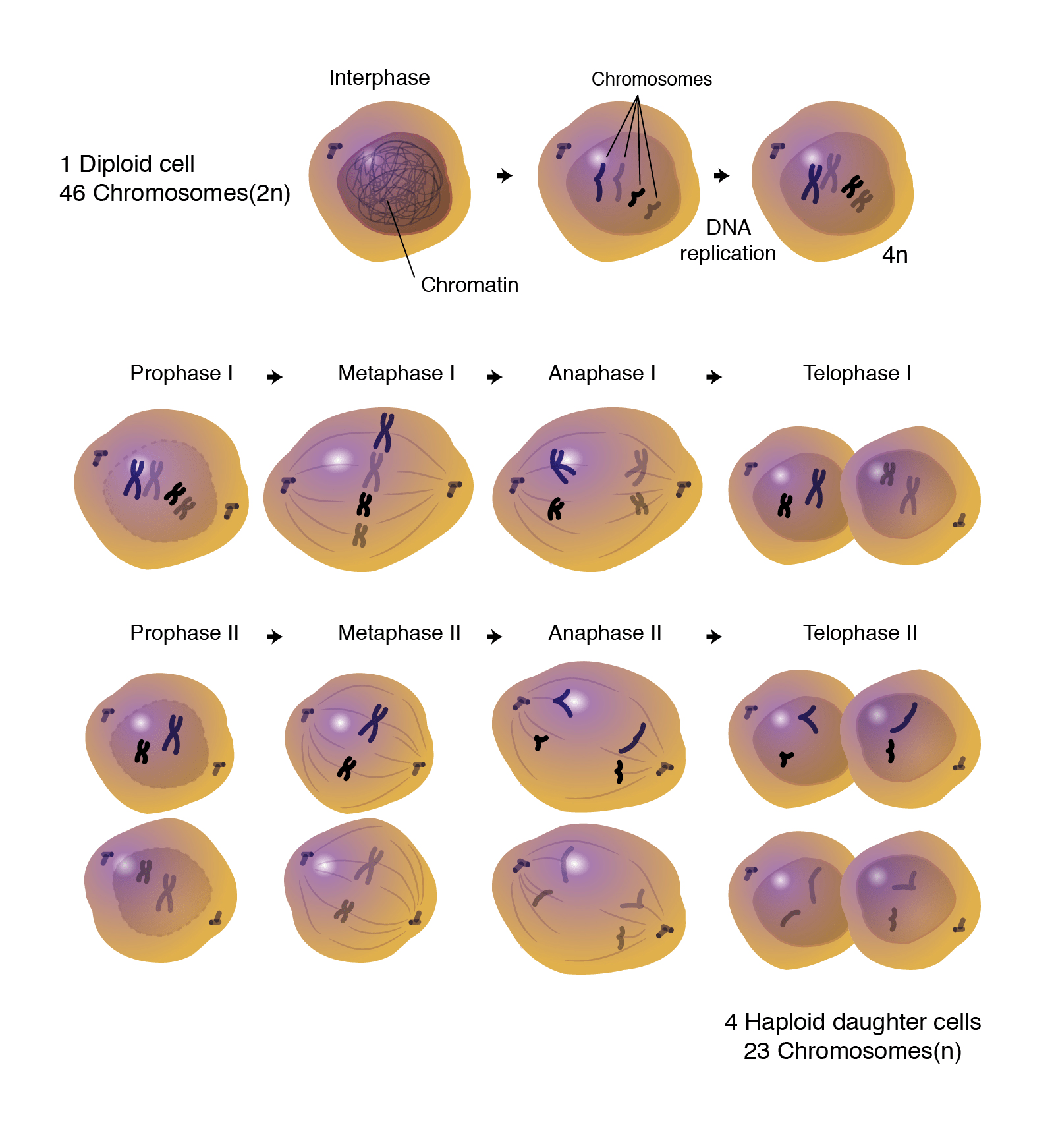
Meiosis I. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is focused on cell growth.
How do the products of meiosis I differ from those of meiosis II? Socratic
Interphase. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase is the first phase of interphase and is focused on cell growth. In the S phase, the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated. Finally, in the G 2 phase, the cell undergoes the final preparations for meiosis.
Meiosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose with Diagram
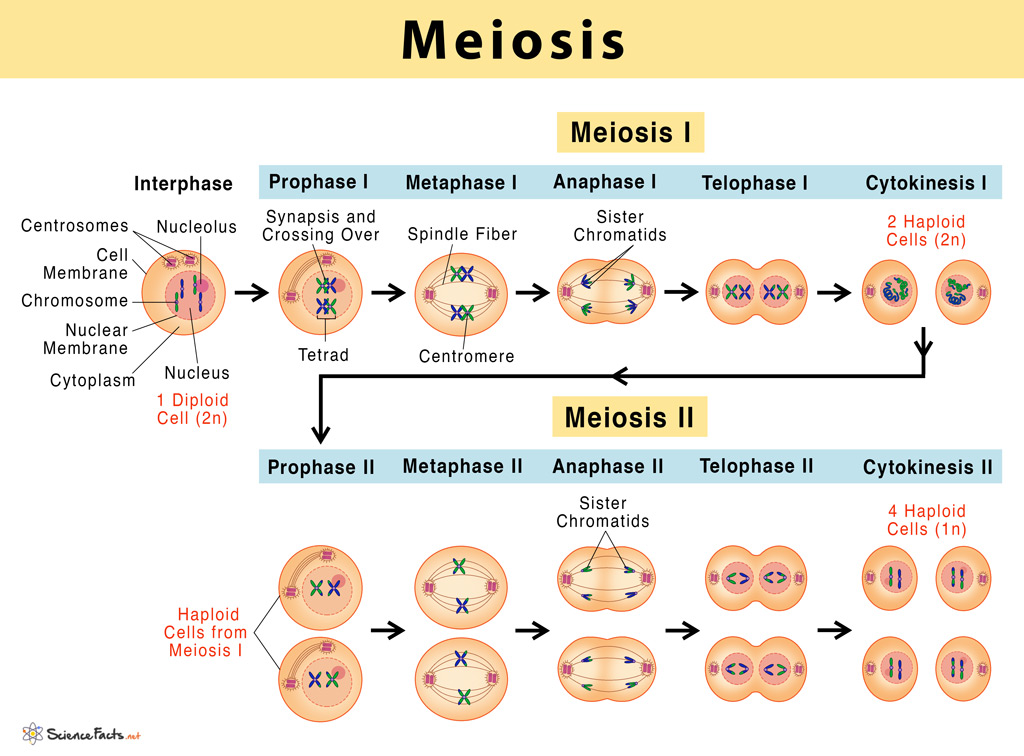
There are 2 parts to the cell cycle: interphase and mitosis/meiosis. Interphase can be further subdivided into Growth 1 (G1), Synthesis (S), and Growth 2 (G2). During the G phases, the cell grows by producing various proteins, and during the S phase, the DNA is replicated so that each chromosome contains two identical sister chromatids (c).

Las 11 fases de la meiosis (y qué sucede en cada una)
Meiosis 1: Meiosis 1 is a heterotypic division, reducing the chromosome number in the daughter cell by half, compared to the parent cell. Meiosis 2: Meiosis 2 is a homotypic division, equalizing the chromosome number of both parent and daughter cells.

What is Meiosis? Phases, Definition,Cell Division, Comparison
This is the phase in which all the "building blocks" for meiosis are prepared. The stages are the G 1 phase (the first "gap" phase), the S phase, and the G 2 phase (the second "gap" phase). G 1 Phase. In the G phases, G stands for "gap." During the G 1 phase, the cell produces the proteins necessary for replicating DNA. S Phase

Meiosis qué es, fases y características Toda Materia
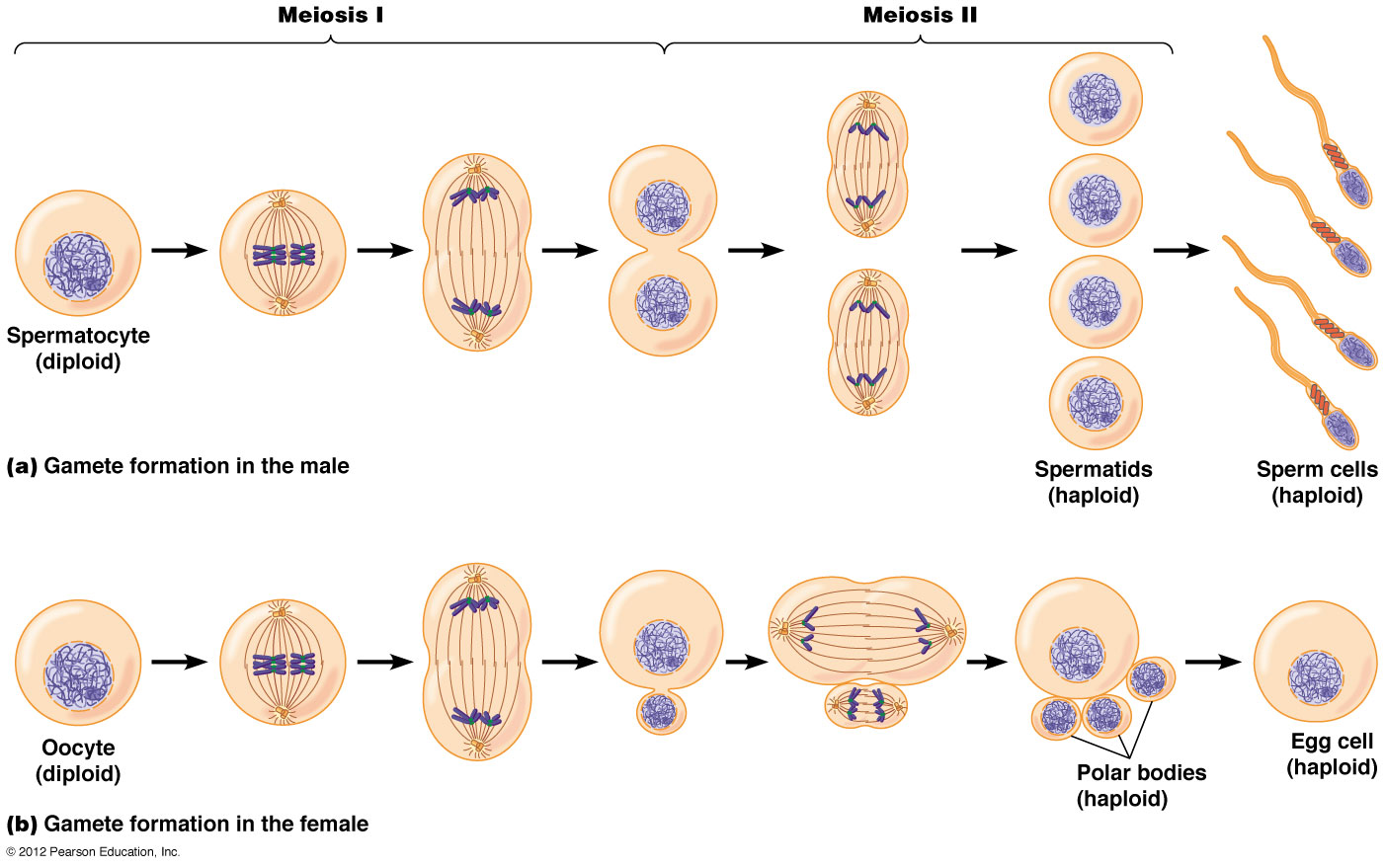
meiosis. produces four genetically unique cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as in the parent. mitosis. produces two genetically identical cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as in the parent. Meiosis begins with a diploid cell, which contains two copies of each chromosome, termed homologs.
FileMeiosis diagram.jpg
Meiosis I. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase (the "first gap phase") is focused on cell growth. During the S phase—the second phase of interphase—the cell copies or replicates the DNA of the chromosomes.
The Process of Meiosis OpenStax Biology 2e
Updated meiosis video. Join the Amoeba Sisters as they explore the meiosis stages with vocabulary including chromosomes, centromeres, centrioles, spindle fib.

nnhsbiology / Meiosis Simplified
And for the amount of chromosomes present after meiosis 1, there are (using the example of an organism with just 2 chromosomes) 2 chromosomes. It duplicated first: 2 chromosomes (1 pair) -> 4 chromosomes (2 pairs) -> 2 chromosomes. This means that there are 2 chromosomes present in each cell (two Xs but the same number of individual chromosomes.

Meiosis 1 and 2 Diagram Diagram Quizlet
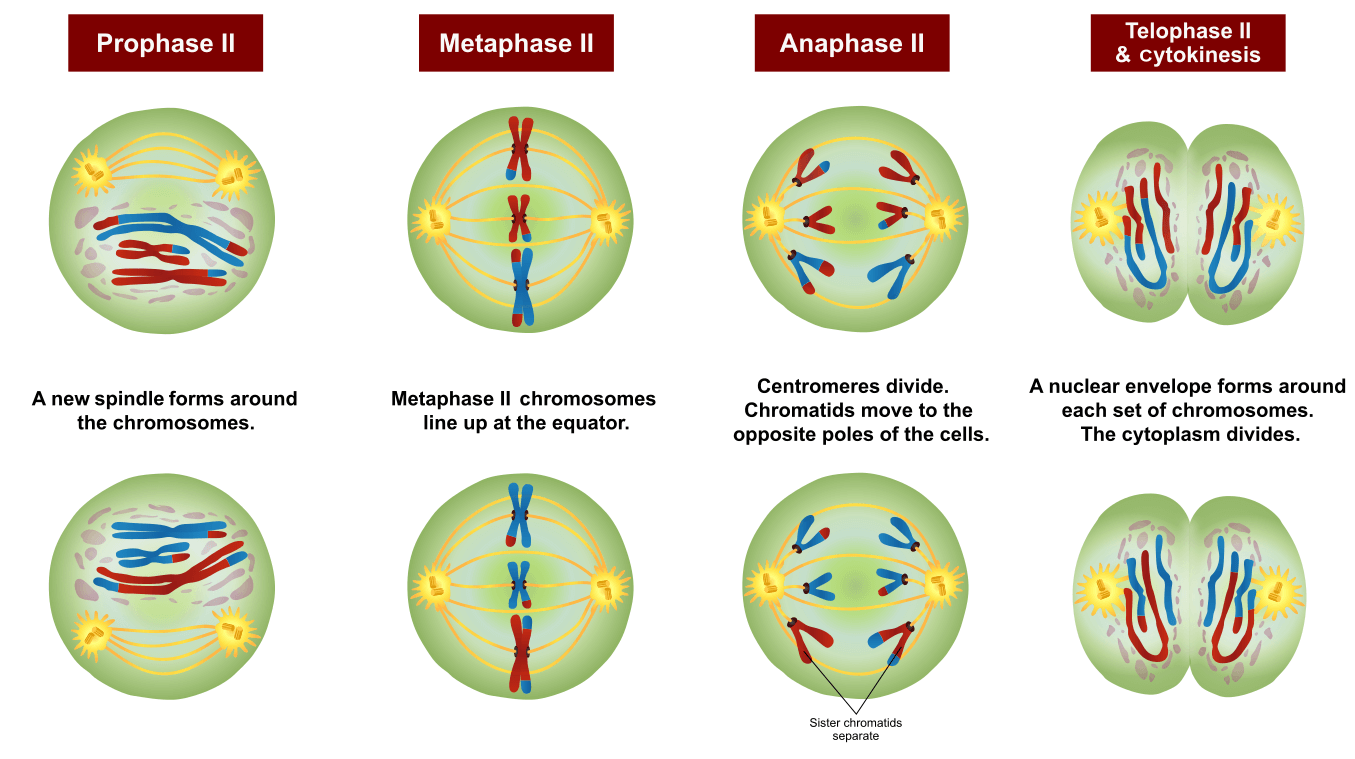
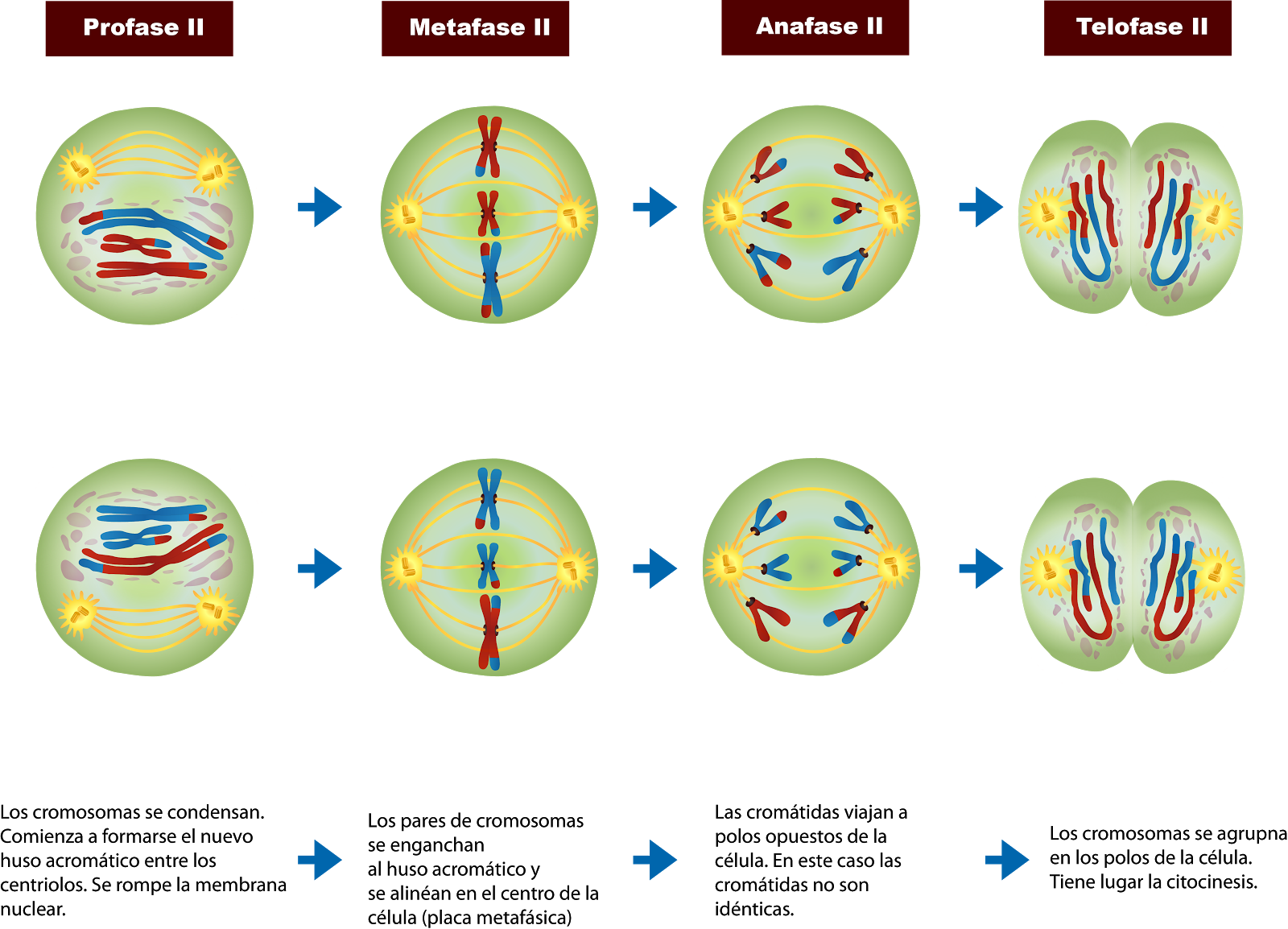
The four stages of meiosis II are as follows:-. Prophase II - It immediately sets off after the cytokinesis when the daughter cells are formed. The chromosomes begin to condense accompanied by the dissolution of the nuclear membrane and the disappearance of the Golgi apparatus and ER complex. Metaphase II - The chromosomes are connected to.
Label The Phases Of Meiosis
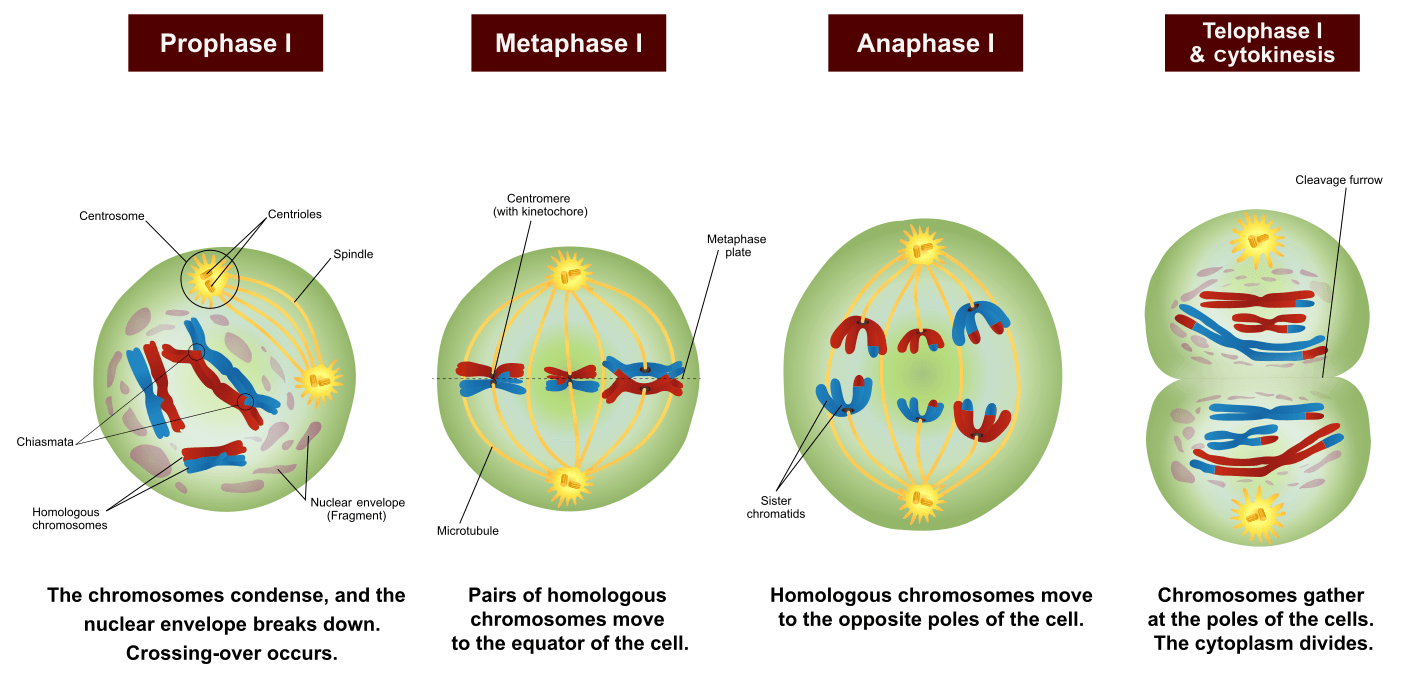
Meiosis I includes crossing over or recombination of genetic material between chromosome pairs, while meiosis II does not. This occurs in meiosis I in a long and complicated prophase I, split into five sub-phases. The equatorial plane in meiosis II is rotates 90° from the alignment of the equatorial plane in meiosis I.
Meiosis Phases, Stages, Applications with Diagram
meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm.
Meiosis Function, Phases and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
To put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. In humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm and eggs. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a complete diploid set: a new genome.
Stages Of Meiosis Simple
Non-kinetochore microtubules elongate the cell. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: Meiosis I vs. Meiosis II: The process of chromosome alignment differs between meiosis I and meiosis II. In prometaphase I, microtubules attach to the fused kinetochores of homologous chromosomes, and the homologous chromosomes are arranged at the midpoint of the cell in.