PPT Geometria Molecular e Interações Químicas Moleculares PowerPoint Presentation ID3560795
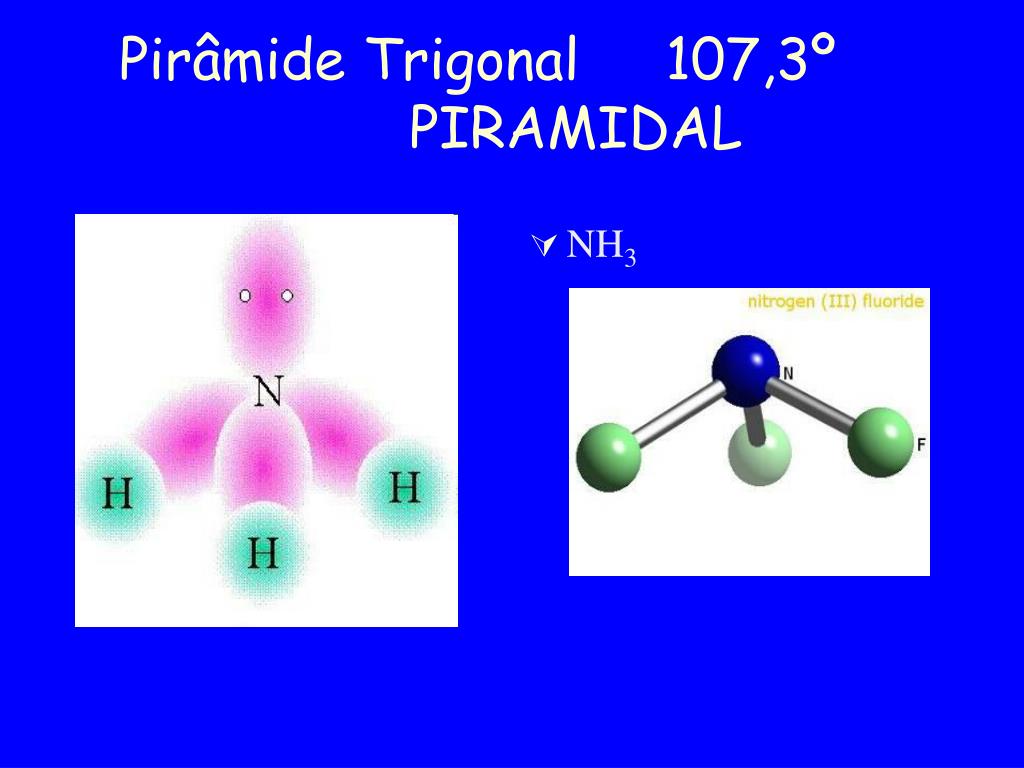
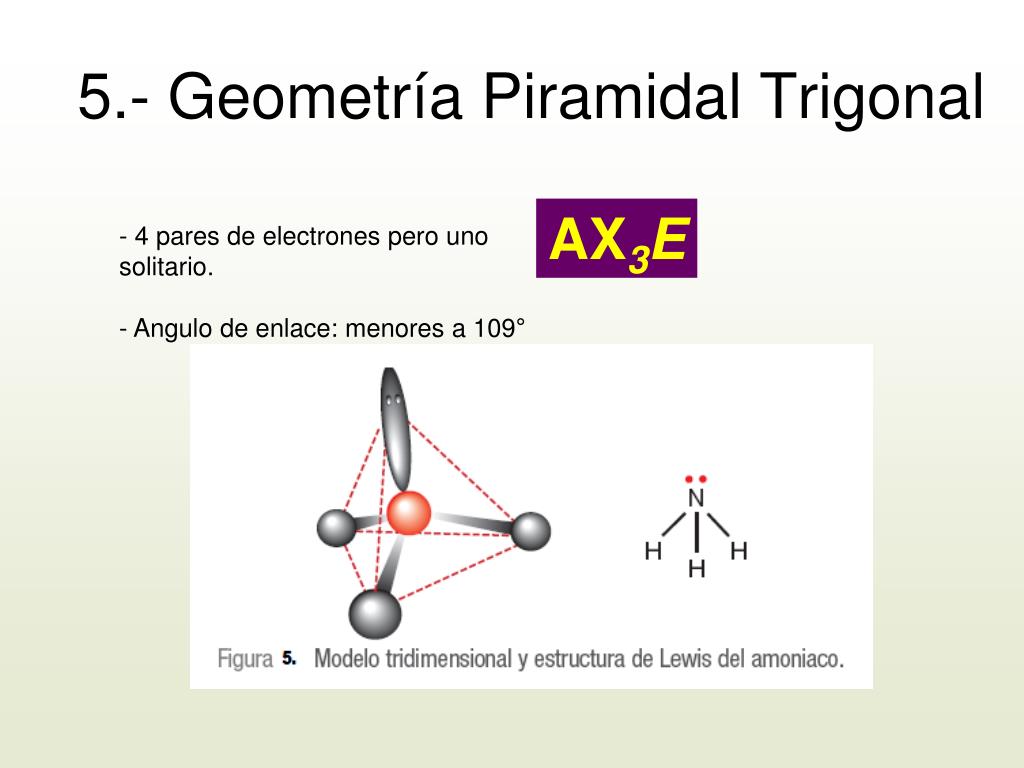
An example of trigonal pyramid molecular geometry that results from tetrahedral electron pair geometry is NH 3. The nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and thus needs 3 more electrons from 3 hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. This then leaves a lone electron pair that is not bonded to any other atom. The three hydrogen atoms and the lone.

Calculando área de una pirámide triangular YouTube
A trigonal bipyramidal molecule is a bit more complicated, mostly because it has more atoms and bonds to take into account. As the name implies, a trigonal bipyramidal shape looks like two three.

Pirâmide Características e fórmulas básicas VouPassar
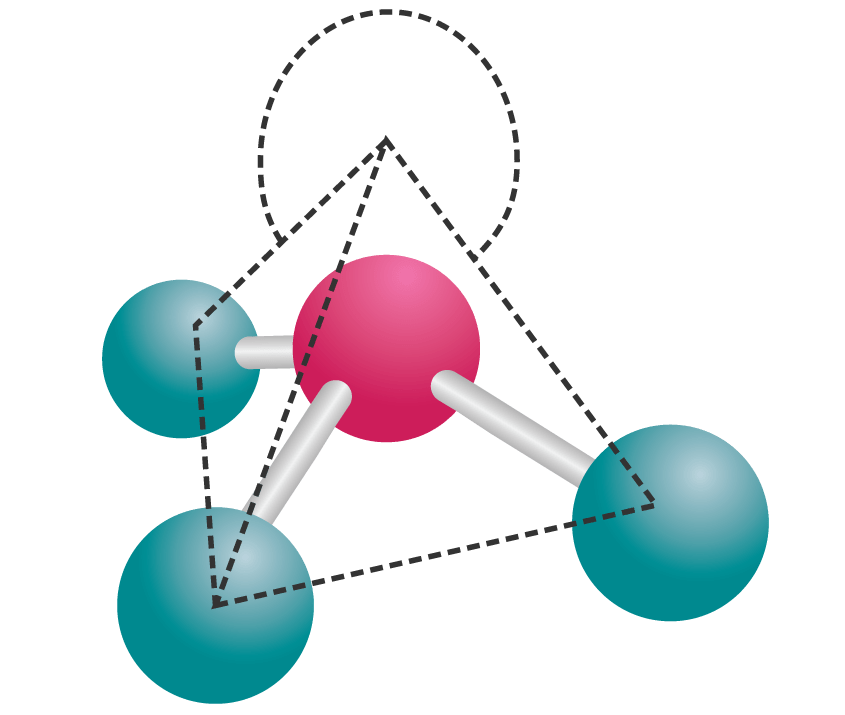
Trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base, resembling a tetrahedron (not to be confused with the tetrahedral geometry ). When all three atoms at the corners are identical, the molecule belongs to point group C3v.

Trigonal pyramid (crystallography) 3 3D model by Museum of Mineralogy and Petrography, UAIC
Other articles where trigonal pyramidal arrangement is discussed: ammonia: Physical properties of ammonia:.The ammonia molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape with the three hydrogen atoms and an unshared pair of electrons attached to the nitrogen atom. It is a polar molecule and is highly associated because of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The dielectric constant of ammonia (22.
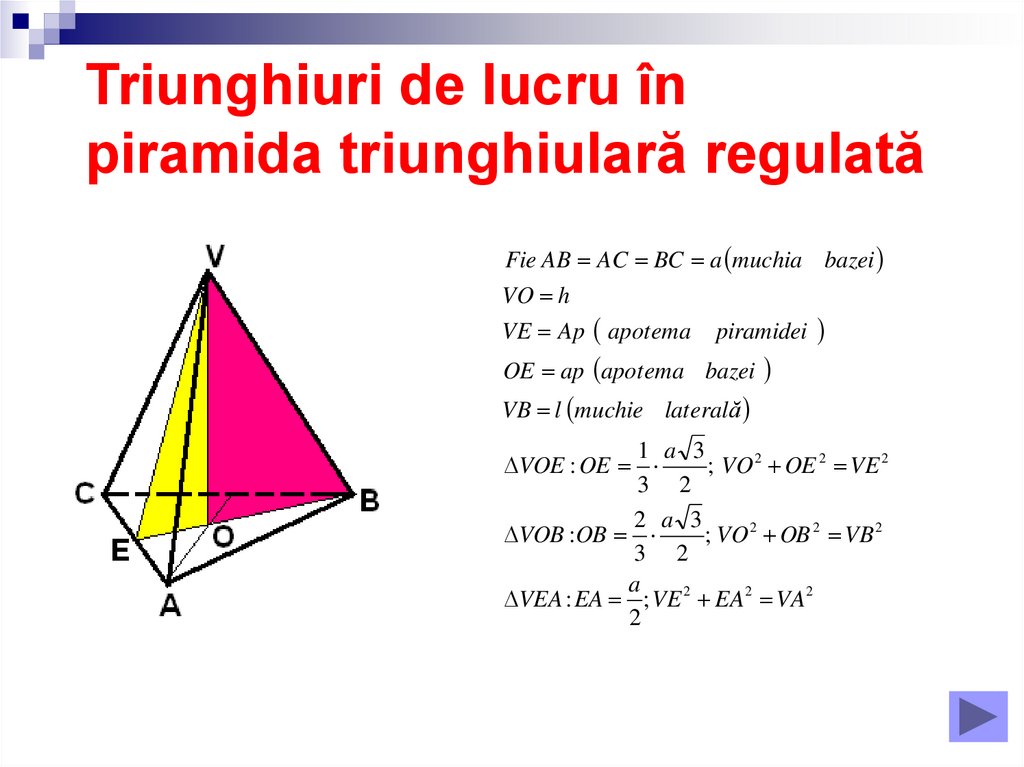
Aria Laterala Piramida Triunghiulara Regulata 8
The trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry that resembles a tetrahedron that has one atom at the apex and three atoms at the trigonal base corners. The molecule belongs to point group C3v because all three atoms present at the corners are equal. A few ions and molecules having trigonal pyramidal geometry are given as the xenon trioxide (XeO3.
terceroespañol Pirámides
In this video we'll look at the Trigonal Pyramidal Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. We'll use the example of NH3 to understand the molecular shape. To.
Trigonal Pyramidal Lewis Dot Structure
Orbit navigation Move camera: 1-finger drag or Left Mouse Button Pan: 2-finger drag or Right Mouse Button or SHIFT+ Left Mouse Button Zoom on object: Double-tap or Double-click on object Zoom out: Double-tap or Double-click on background Zoom: Pinch in/out or Mousewheel or CTRL + Left Mouse Button

Molecular Geometry at Kaplan University (MO) StudyBlue
Trigonal pyramidal is a geometry of some molecules like ammonia and phosphine. Let us an example of ammonia to understand the trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry. Ammonia is an inorganic compound with three hydrogen atoms surrounding one nitrogen atom. All three hydrogen atoms shared their valence electrons with the nitrogen atom forming three strong covalent bonds. […]

Pirámide triángulo ostrosłup prawidłowy borde plano, pirámide, ángulo, cara, simetría png PNGWing
In a rigorous geometrical sense, there is no difference between tetrahedron and trigonal pyramid--the terms both mean the same thing.In colloquial and chemical use, however, 'tetrahedron' typically implies the 'regular tetrahedron', where all four faces are equilateral triangles. Chemically speaking, when referring to these two shapes as descriptors of molecular geometries, there is (usually.

Pyramid (geometry) Wikipedia
En geometría molecular , el número de enlaces y pares de electrones solitarios determina la forma de una molécula. Usando una definición estricta de bipiramidal trigonal , hay un átomo central unido a cinco átomos circundantes y no hay pares de electrones solitarios. Sin embargo, algunas definiciones permiten pares de electrones solitarios.

Elongated Trigonal Pyramid Triangle Clipart Large Size Png Image PikPng
Pharmaceutical and Medicine Manufacturing Newspaper, Periodical, Book, and Directory Publishers Media Streaming Distribution Services, Social Networks, and Other Media Networks and Content Providers Scientific Research and Development Services Business Support Services Soap, Cleaning Compound, and Toilet Preparation Manufacturing Miscellaneous Nondurable Goods Merchant Wholesalers Drugs and.
Trigonal Pyramidal Examples
The difference between trigonal planar and trigonal pyramidal can be seen in the structure of a molecule. Trigonal planar does not have a lone pair of electrons while trigonal pyramidal has a lone pair in the central atom. Also, all the atoms of a planar molecule lie in the same plane unlike the atoms of pyramidal.

piramida triunghiulara regulata Mate Pedia
An example of an ideal molecule with trigonal planar is Boron trifluoride. Examples of inorganic anions that show trigonal planar are carbonates and sulfates. Other complex compounds that normally surround central atoms are three NH2 groups and tend to be bind on the central atom. Differences Between Trigonal Planar and Trigonal Pyramidal
Jelaskan arti dari istilah berikut! f. Piramida...
A pyramid is a polyhedron that may be formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form an isosceles triangle, called a lateral face. [3] The edges connected from the polygonal base's vertices to the apex are called lateral edges. [4] Historically, the definition of a pyramid has been described by.

Piramida triunghiulara, tetraedrul descriere si reprezentare Mate Pedia
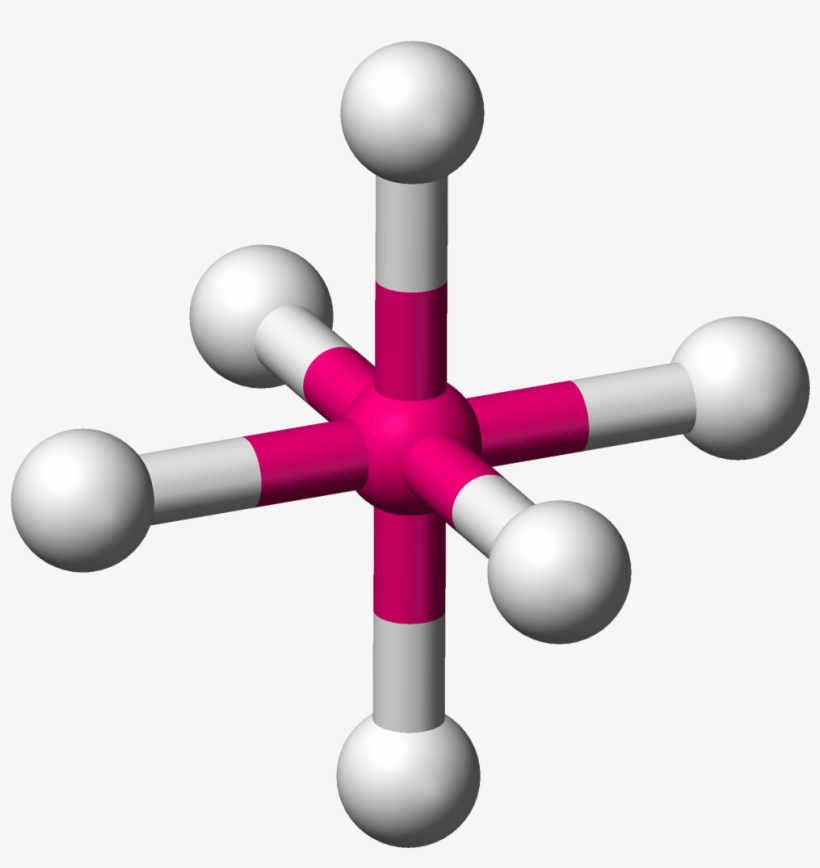
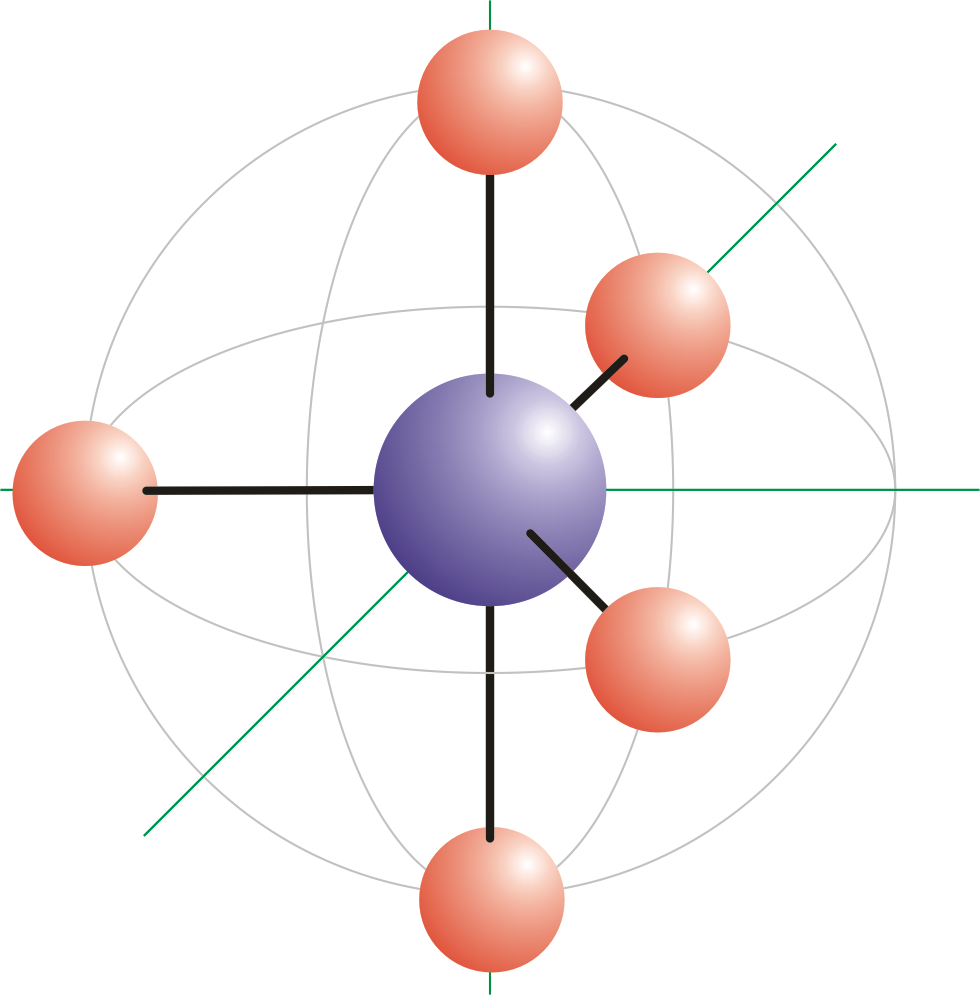
Trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry. In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. [1] This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid ), because there is.
PPT Enlace Químico PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5777686
Stereoisomers. Since there are two types of atoms on a Trigonal Bipyramidal structure, axial and equatorial, there are different Stereoisomers that could arise depending on the substituents attached. For example, if there is 4 X atoms and 1 Y atom attached to the central atom, Y could either be in an equatorial position or in an axial position.