
cos(A+B)=cos(A)cos(B)sin(A)sin(B) proof geometrical ข้อมูลทั้งหมดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับcos a cos
Nothing further can be done with this topic. Please check the expression entered or try another topic. sin(A)cos(B) +cos(A)sin(B) sin ( A) cos ( B) + cos ( A) sin ( B) Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.
SinA+sinB=a and cosA cosB=b then tan(A B)/2?
Example 2: Using the values of angles from the trigonometric table, solve the expression: 2 sin 67.5º cos 22.5º. Solution: We can rewrite the given expression as, 2 sin 67.5º cos 22.5º = 2 sin ½ (135)º cos ½ (45)º. Assuming A + B = 135º, A - B = 45º and solving for A and B, we get, A = 90º and B = 45º.. ⇒ 2 sin ½ (135)º cos ½ (45)º = 2 sin ½ (90º + 45º) cos ½ (90º - 45º)
79. Sin A=3/5 and cos B=9/41,A is greater than 0 and less than 90 ,then b is greater than 90 and
Here is the list of formulas for Class 11 students as per the NCERT curriculum. All the formulas of trigonometry chapter are provided here for students to help them solve problems quickly. Trigonometry Formulas. sin (−θ) = −sin θ. cos (−θ) = cos θ.

sin ( AB ) = sin A cos B cosA sinB proof Trigonometry By J.P. Verma YouTube
Example 2: Express the trigonometric function sin 3x cos 9x as a sum of the sine function using sin a cos b formula. Solution: We will use the sin a cos b formula: sin a cos b = (1/2) [sin (a + b) + sin (a - b)]. Identify the values of a and b in the formula. We have sin 3x cos 9x, here a = 3x, b = 9x. Substitute the values of a and b in the formula sin a cos b = (1/2) [sin (a + b) + sin (a - b)]

prove that sin (A+B)+sin (AB)/ cos (A+B)+cos (AB) = tan A Maths Trigonometric Functions
The following (particularly the first of the three below) are called "Pythagorean" identities. sin 2 ( t) + cos 2 ( t) = 1. tan 2 ( t) + 1 = sec 2 ( t) 1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement. Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider.

If sin A = sin B and cos A = cos B, then prove that A = 2nπ + B for some integer n. Brainly.in
Learn the proof of sin (A+B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B. Learn to derive formula of sin (A +B). This is a very important and frequently used formula in trig.

7 TRIGONOMETRY ( PRODUCT FORMULA SIN(A+B).SIN(AB),COS ALSO AND SOME IMPORTANT TRICK) YouTube
Here's a proof I just came up with that the angle addition formula for sin () applies to angles in the second quadrant: Given: pi/2 < a < pi and pi/2 < b < pi // a and b are obtuse angles less than 180°. Define: c = a - pi/2 and d = b - pi/2 // c and d are acute angles.

cos(ab)=cosacosb+sinasinb proof YouTube
In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc. Some formulas including the sign of ratios in different quadrants, involving co-function identities (shifting angles), sum & difference identities, double angle identities.
37. sin(B+A) + cos(B A)/ sin(B A) + cos(B+A) is equal to 1. cosB + sinB/cosB sinB 2. cosA + sinA
prove: cos\left(a+b\right)cos\left(a-b\right)=cos^{2}a-sin^{2}b. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. High School Math Solutions - Trigonometry Calculator, Trig Identities. In a previous post, we talked about trig simplification. Trig identities are very similar to this concept. An identity.

Sin A + cos B = 1, A = 30 and B is acute angle, then find value of B
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Découvrir 112+ imagen cos sin formule fr.thptnganamst.edu.vn
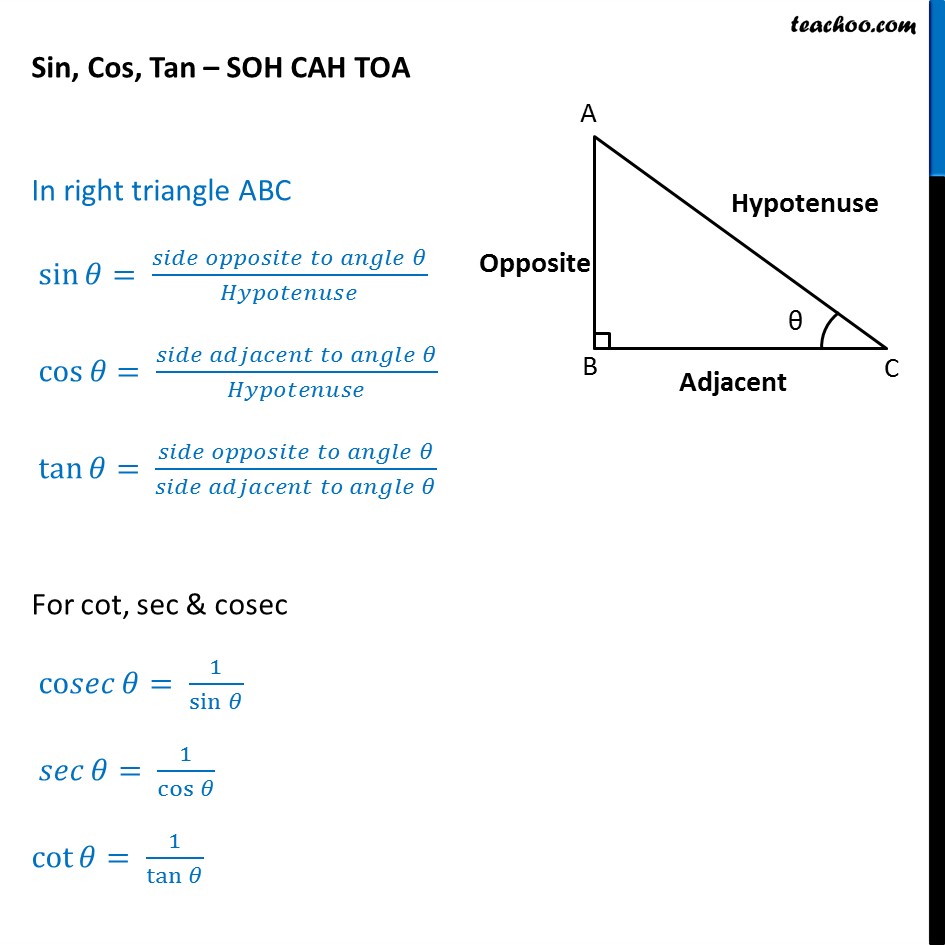
It uses functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent to describe the ratios of the sides of a right triangle based on its angles. What are the 3 types of trigonometry functions? The three basic trigonometric functions are: Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), and Tangent (tan).

29. If A = 60° and B = 30°, find the value of(sin A cos B + cos A sin B)2 + (cos A cos B sin A
The three main functions in trigonometry are Sine, Cosine and Tangent. They are just the length of one side divided by another. For a right triangle with an angle θ : Sine Function: sin (θ) = Opposite / Hypotenuse. Cosine Function: cos (θ) = Adjacent / Hypotenuse. Tangent Function: tan (θ) = Opposite / Adjacent.

If cos A + sin B = m and sin A + cos B = n , prove that 2 sin (A + B) = m^2 + n^2 2.
that cos( B) = cosB(cos is even) and sin( B) = sinB(sin is odd). Similarly (7) comes from (6). (8) is obtained by dividing (6) by (4) and dividing top and bottom by cosAcosB, while (9) is obtained by dividing (7) by (5) and dividing top and bottom by cosAcosB. (10), (11), and (12) are special cases of (4), (6), and (8) obtained by putting A= B.

Démonstration de cos(a)cos(b), sin(a)sin(b) et sin(a)cos(b) YouTube
\int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} Show More; Description. Solve problems from Pre Algebra to Calculus step-by-step . step-by-step \cos(a)\cos(b)-\sin(a)\sin(b) en. Related Symbolab blog posts. Practice Makes Perfect. Learning math takes practice, lots of practice. Just like running, it takes practice.

32 FORMULA FOR 2 SIN(A)COS(B), FORMULA 2 SIN(A)COS(B) FOR Chemical
The Law of Sines. The Law of Sines (or Sine Rule) is very useful for solving triangles: a sin A = b sin B = c sin C. It works for any triangle: a, b and c are sides. A, B and C are angles. (Side a faces angle A, side b faces angle B and. side c faces angle C).
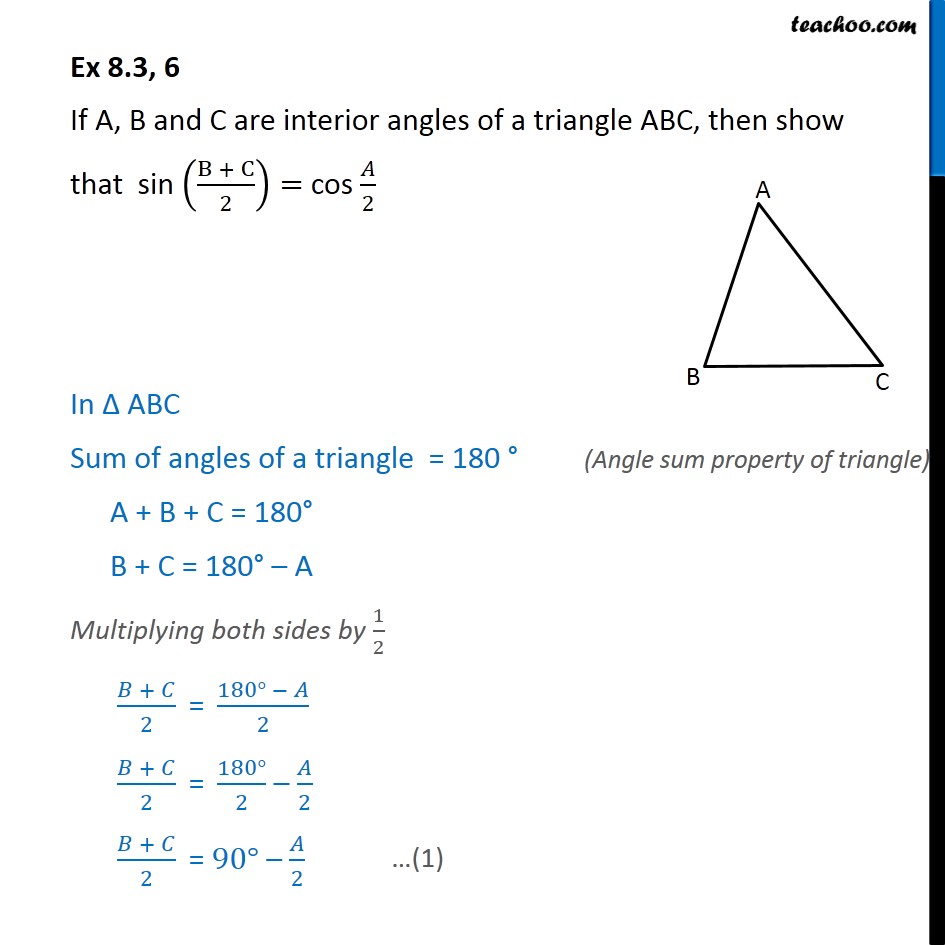
Question 6 Show that sin (B + C / 2) = cos A/2 Chapter 8 Class 10
sin(A+B) = sinAcosB +cosAsinB (2) cos(A+B) = cosAcosB −sinAsinB (3) Using these we can derive many other identities. Even if we commit the other useful identities to memory, these three will help be sure that our signs are correct, etc. 2 Two more easy identities