
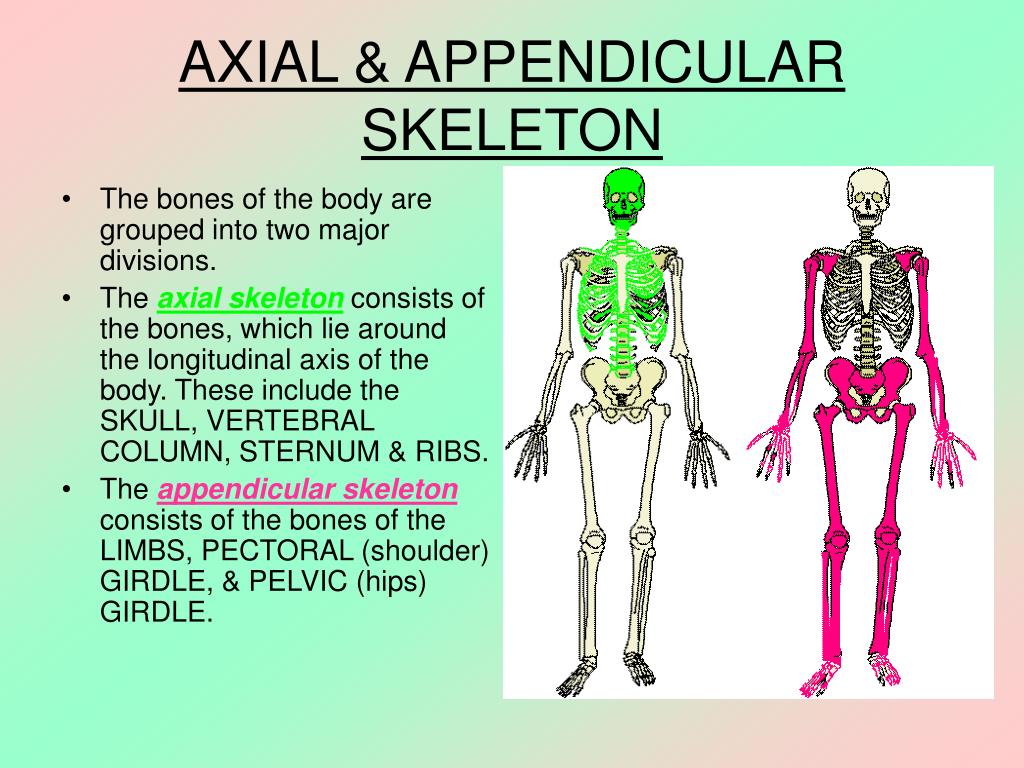
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
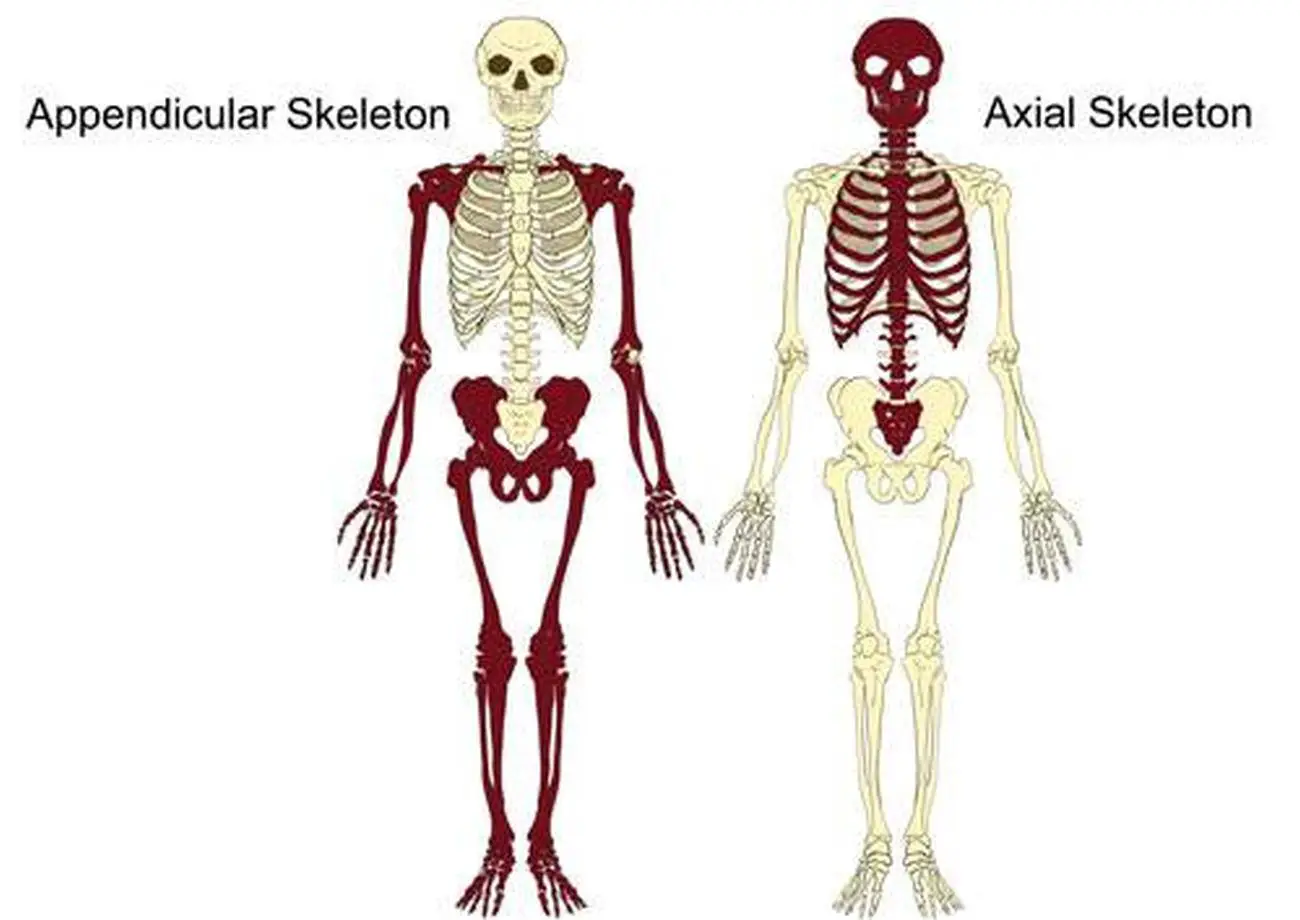
The axial skeleton comprises the bones found along the central axis traveling down the center of the body. The appendicular skeleton comprises the bones appended to the central axis. Above: The bones of the axial skeleton make up the central axis of the body including the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, sacrum, and coccyx.

secara garis besar kerangka manusia Gavin Dyer
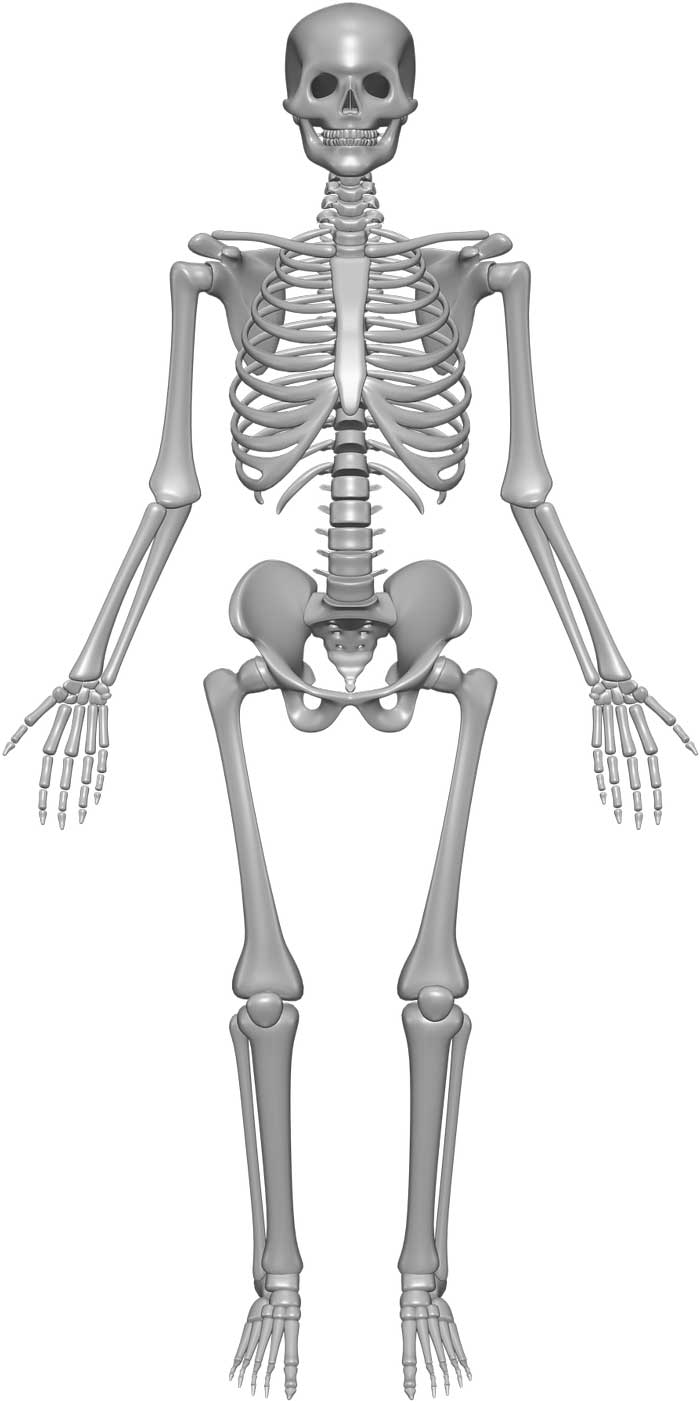
Axial Skeleton. Your axial skeleton is made up of the 80 bones within the central core of your body. This includes bones in your skull (cranial and facial bones), ears, neck, back (vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone) and ribcage (sternum and ribs). Your axial skeleton protects your brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs and other important organs.
Skeleton System (Structure + Composition + Facts) Science4Fun
The Axial Skeleton. The axial skeleton forms the vertical, central axis of the body and includes all bones of the head, neck, chest, and back (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). It serves to protect the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. It also serves as the attachment site for muscles that move the head, neck, and back, and for muscles that act across the shoulder and hip joints to move their.
Biologi Rangka Manusia Pahamify Taklukkan UTBK
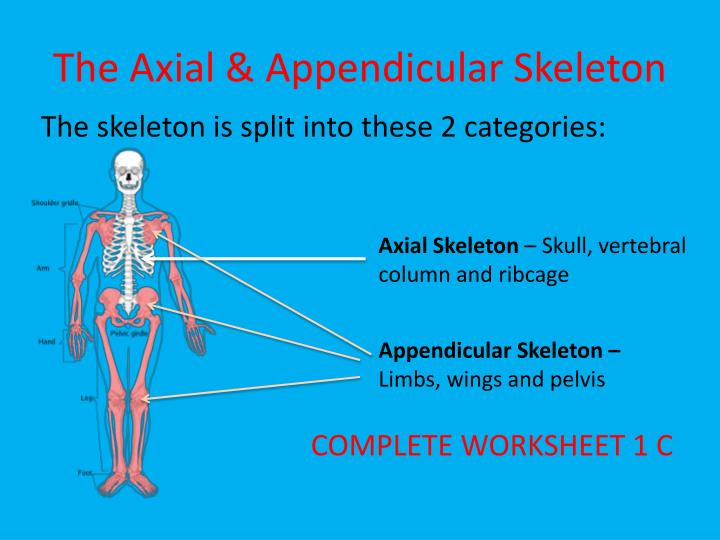
The axial skeleton forms a vertical axis and the appendicular skeleton includes all of the bones of the upper and lower limbs plus the bones that anchor each limb to the axial skeleton 6.3: The Skull In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit.

Major Bones Of The Axial Skeleton
Fig. 7.1: Axial and Appendicular Skeleton . The axial skeleton of the adult consists of 80 bones, including the skull, the vertebral column, and the thoracic cage.The axial skeleton forms the longitudinal axis of the body, the center or midline of the body around which the limbs rotate, much as the earth spins around its center axis. Additionally, the axial skeleton supports the head, neck.

Image result for axial skeleton anatomy labeled Human Skeleton Anatomy, Human Body Anatomy
Bones make up the skeletal system of the human body and are responsible for somatic rigidity, storage of different micronutrients, and housing bone marrow. W.

Mengenal Anatomi Tulang Manusia, Disusun Rangka Aksial dan Apendikular Fisiohome
The axial skeleton includes the bones that form the skull, laryngeal skeleton, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The bones of the appendicular skeleton (the limbs and girdles) "append" to the axial skeleton. 1. Skull Bones Protect the Brain and Form an Entrance to the Body. The skull consists of the cranial bones and the facial skeleton.

Rangka Aksial dan Rangka Apendikular (Rangkuman Materi Sistem Gerak Part3)
The human axial skeleton consists of 81 different bones. It is the medial core of the body and connects the pelvis to the body, where the appendix skeleton attaches. As the skeleton grows older the bones get weaker with the exception of the skull. The skull remains strong to protect the brain from injury. In humans, the axial skeleton serves to.
Pictures Of Axial Skeleton
The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain, the spinal cord, and the organs in the ventral body cavity. It provides a surface for the attachment of muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk, performs respiratory movements, and stabilizes parts of the appendicular skeleton. Figure 1.

Divisions of appendicular and axial skeletal system labeled explanation Skeletal system
The axial skeleton serves primarily to support and protect the heart, lungs, and central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The axial skeleton differs from the appendicular skeleton, which is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs. In humans, the axial skeleton is made up of 80 individual bones.
Axial And Appendicular Skeleton Joints
The appendicular skeleton includes all of the limb bones, plus the bones that unite each limb with the axial skeleton. The bones that attach each upper limb to the axial skeleton form the pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle). This consists of two bones, the scapula and clavicle. The clavicle (collarbone) is an S-shaped bone located on the anterior.

Tulang Penyusun Rangka Tubuh Manusia AGM MEDICA
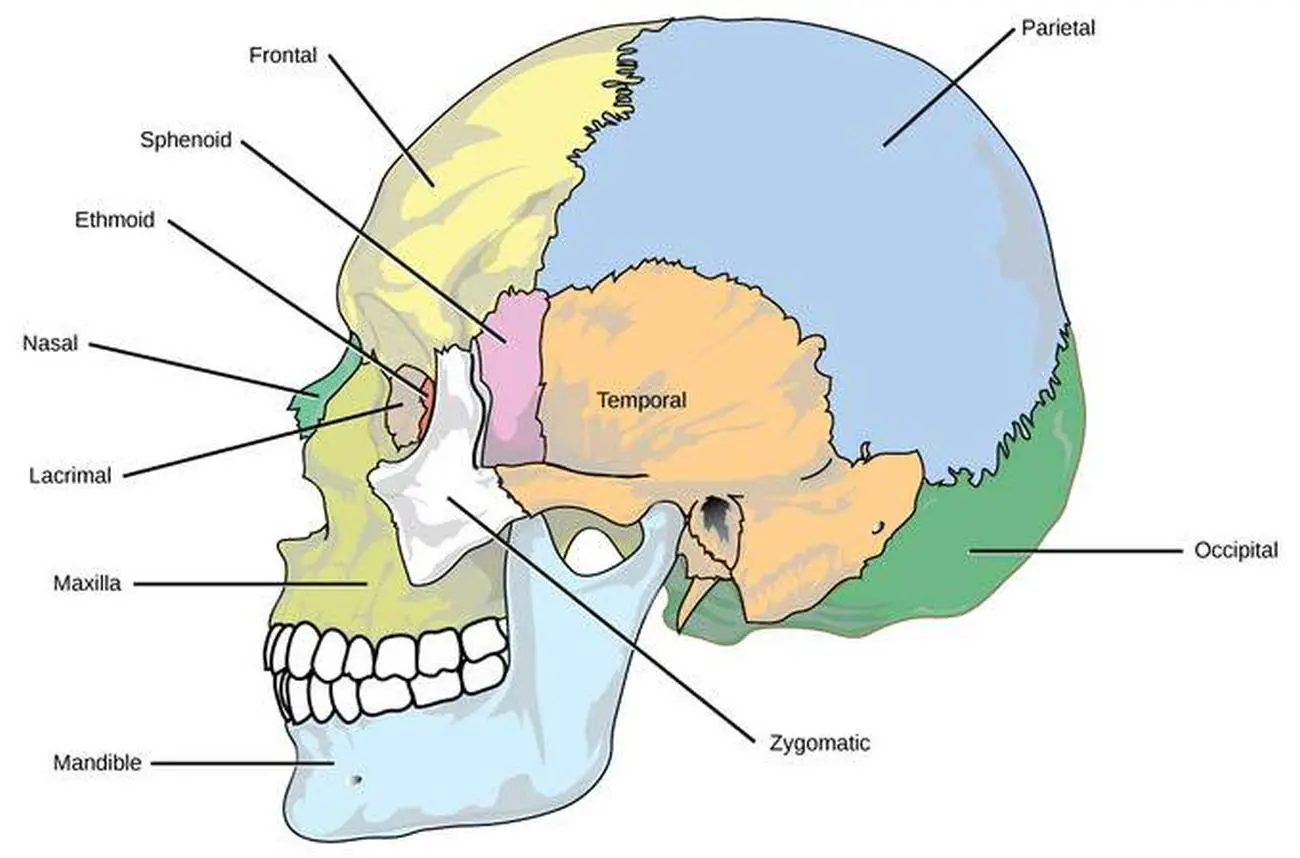
The 14 facial bones are the nasal bones, maxillary bones, zygomatic bones, palatine, vomer, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, and mandible. Figure 38.3.1 38.3. 1: Cranial and facial bones: The facial bones of the skull form the face and provide cavities for the eyes, nose, and mouth. The cranial bones, including the frontal, parietal.

Axial Skeleton Development Medical Embryology Video Lecture VLearning YouTube
The axial skeleton consists of all the bones in the central part of your body. This includes everything from your skull and ears to your neck, breastbone (sternum), spine, and ribcage. There are 80 bones in the axial skeleton. They protect important organs and structures in your body such as your brain, heart, lungs, and spinal cord.
Axial And Appendicular Skeleton Labeling
The axial skeleton is the central portion of the bony skeleton comprising the head, neck and trunk (80 bones in total). It has many functions including housing and protecting the central nervous system as well as the organs of the chest, abdomen and pelvis. It enables movement and supports the upper and lower limbs ( appendicular skeleton ).

Skeleton Aksial
The atlantoaxial joint is a complex joint between the atlas (C1) and the axis (C2). It is composed of three synovial joints; one median atlantoaxial joint and two lateral atlantoaxial joints . The median atlantoaxial joint is formed between the dens of axis and an osteoligamentous ring of the atlas anteriorly and transverse ligament posteriorly.
Pictures Of Axial Skeleton
The skeletal system forms the rigid internal framework of the body. It consists of the bones, cartilages, and ligaments. Bones support the weight of the body, allow for body movements, and protect internal organs. Cartilage provides flexible strength and support for body structures such as the thoracic cage, the external ear, and the trachea.