
What is DNA? Facts
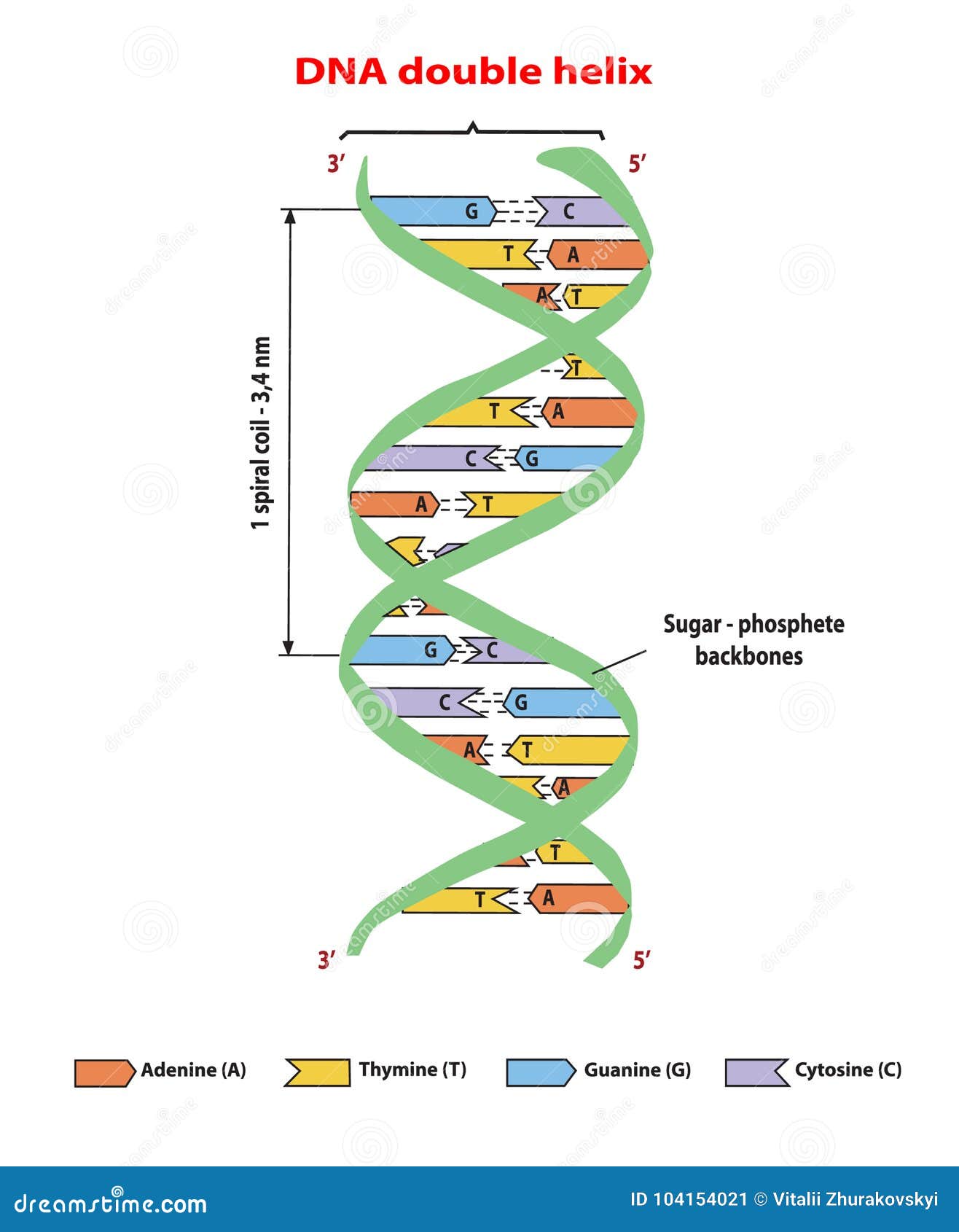
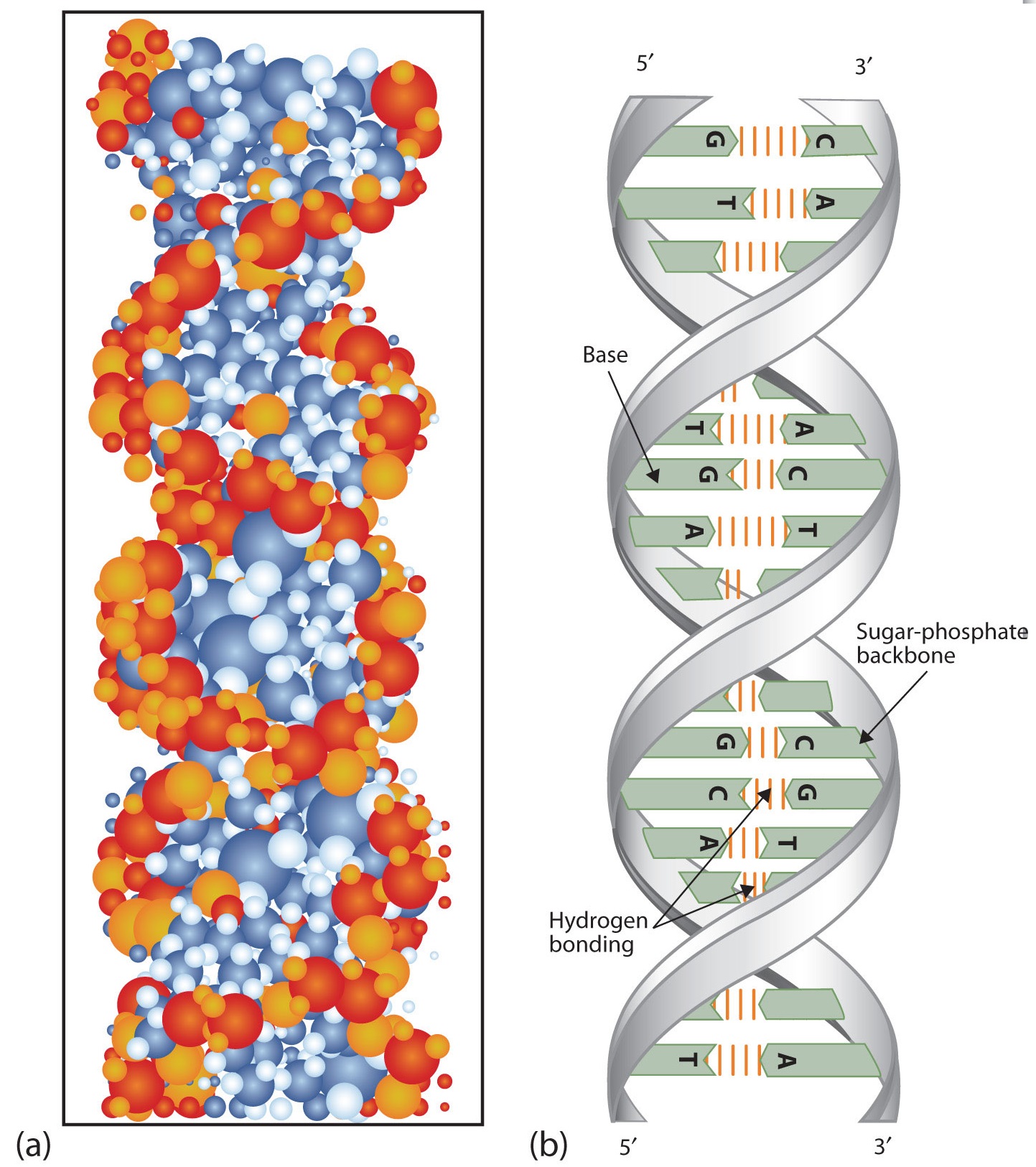
Figure 9.4 DNA (a) forms a double stranded helix, and (b) adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. (credit a: modification of work by Jerome Walker, Dennis Myts) The Structure of RNA. There is a second nucleic acid in all cells called ribonucleic acid, or RNA. Like DNA, RNA is a polymer of nucleotides.

The Structure of DNA Mooramo
AboutTranscript. DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the DNA ladder. Created by Sal Khan.
Dna Double Helix Structure Diagram
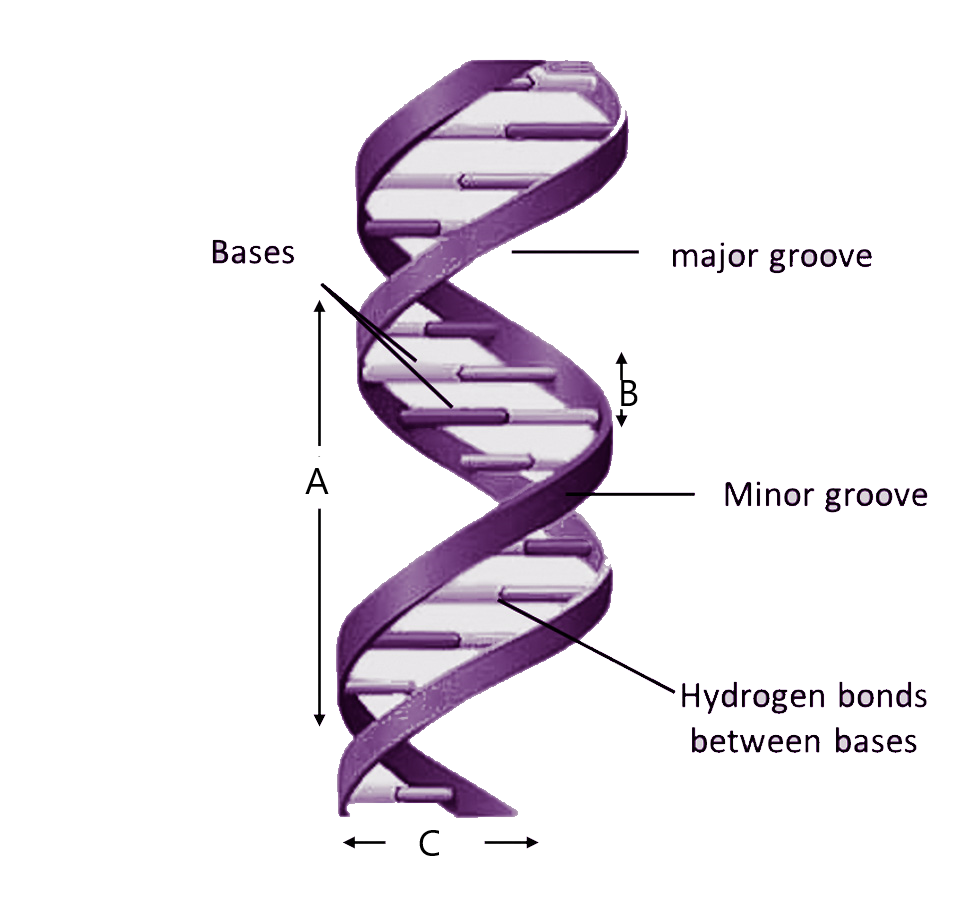
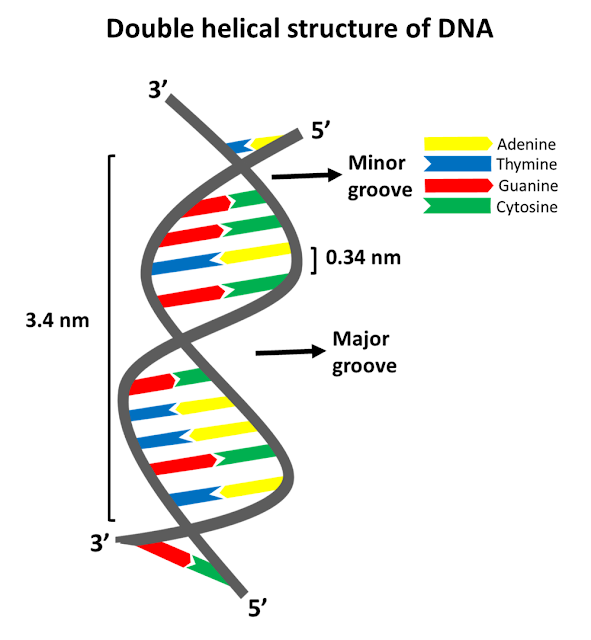
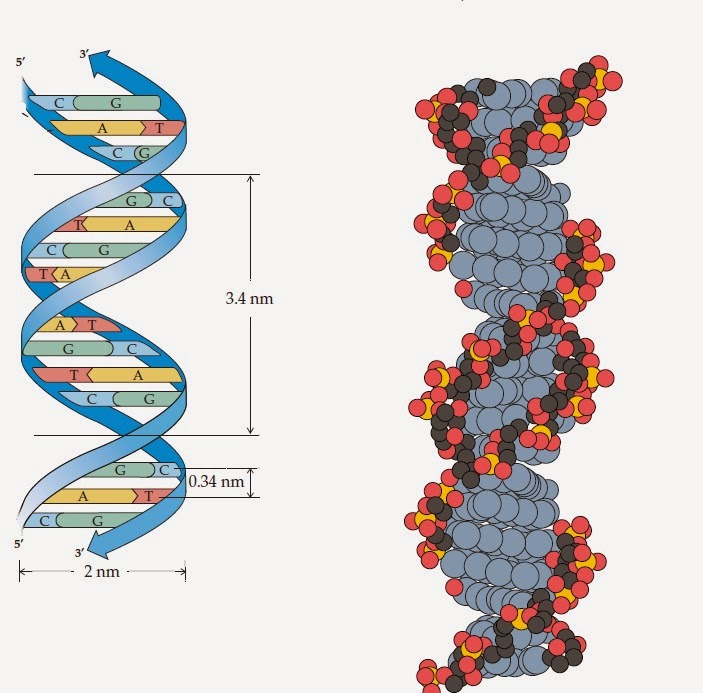
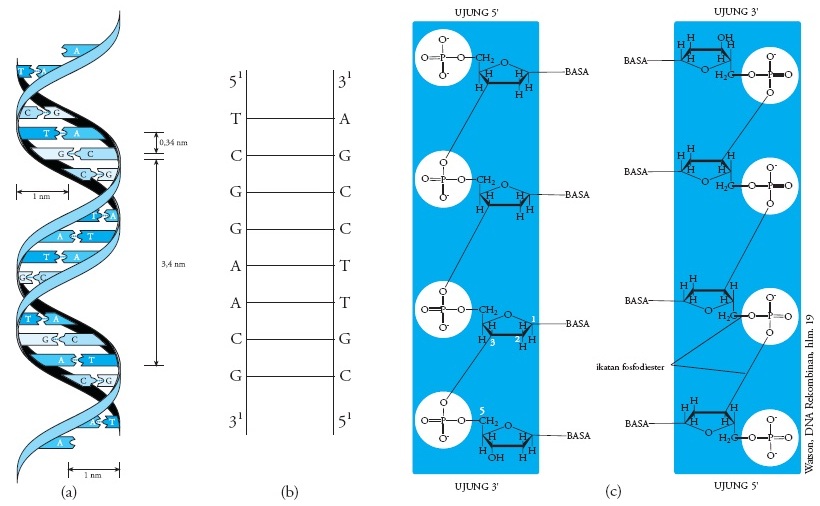
Image of a DNA double helix, illustrating its right-handed structure. The major groove is a wider gap that spirals up the length of the molecule, while the minor groove is a smaller gap that runs in parallel to the major groove. The base pairs are found in the center of the helix, while the sugar-phosphate backbones run along the outside.

Double Helix The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Definition. Double helix, as related to genomics, is a term used to describe the physical structure of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
DNA Structure Double Helix on White Background. Nucleotide, Phosphate, Sugar, and Bases
Figure 1 | The DNA double helix. This drawing appeared in Watson and Crick's report 1 of the structure of DNA, and was produced by Crick's wife, Odile.
Double Helical Structure of DNA Watson and Crick Model Structure of nucleotides
In biology, "double helix" is a term used to describe the structure of DNA. A DNA double helix consists of two spiral chains of deoxyribonucleic acid. The shape is similar to that of a spiral staircase. DNA is a nucleic acid composed of nitrogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine), a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and phosphate.
Dna Double Helix Structure Photograph by Alfred Pasieka/science Photo Library Fine Art America
The two strands of the helix run in opposite directions. This antiparallel orientation is important to DNA replication and in many nucleic acid interactions. Figure 3.12.1 3.12. 1: DNA is a Double Helix: Native DNA is an antiparallel double helix. The phosphate backbone (indicated by the curvy lines) is on the outside, and the bases are on the.
23.7 DNA Replication, the Double Helix, and Protein Synthesis Chemistry LibreTexts
The structure of DNA is a double-helix polymer, a spiral consisting of two DNA strands twisted around each other. James Watson and Francis Crick determined this structure in 1953, building upon almost a century's worth of research from the scientific community. Their work was influenced in particular by two developments: first, the conclusion.
Biology learnspot The structure of DNADouble helical model
In a double helix structure, the strands of DNA run antiparallel, meaning the 5' end of one DNA strand is parallel with the 3' end of the other DNA strand. Diagram showing how the two strands of double stranded DNA runs anti-parallel to each other. One strand runs in a 3' to 5' direction while the other runs in a 5' to 3' direction.

Double Helix The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
The double-helix model of DNA structure was first published in the journal Nature by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, (X,Y,Z coordinates in 1954) based on the work of Rosalind Franklin and her student Raymond Gosling, who took the crucial X-ray diffraction image of DNA labeled as "Photo 51", and Maurice Wilkins, Alexander Stokes, and Herbert Wilson, and base-pairing chemical and.

DNA double helix structure animation YouTube
A. Barrington Brown/Science Source. By Science News. January 20, 1953 at 1:35 pm. James Watson (left) and Francis Crick (right) report in Nature the discovery of the double-helix structure of the.
Struktur Kimia DNA
The DNA is twisted beyond the double helix in what is known as supercoiling. Some proteins are known to be involved in the supercoiling; other proteins and enzymes help in maintaining the supercoiled structure. Eukaryotes, whose chromosomes each consist of a linear DNA molecule, employ a different type of packing strategy to fit their DNA.

DNA Double Helix Labeled Diagram
The double helix is a description of the molecular shape of a double-stranded DNA molecule. In 1953, Francis Crick and James Watson first described the molecular structure of DNA, which they.

1 Schematic representation of doublestranded DNA. The double helix... Download Scientific Diagram
And you go to 1944 and Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod are able to show some pretty good evidence that the actual principle, the thing that was left in that heat-killed bacteria, was probably DNA. And then we get even more conclusive evidence with the experiments of Hershey and Chase and we have a whole video on this.

Structure Of DNA Function, Summary, Diagram & Model
The Double Helix. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are composed of two different classes of nitrogen-containing bases: the purines and pyrimidines. The most commonly occurring purines in DNA are adenine and guanine: Figure 1.2.1: Purines. The most commonly occurring pyrimidines in DNA are cytosine and thymine:

Dna Is Described Best as a Double Helix
Watson and Crick's postulation in 1953, exactly 50 years ago, of a double helical structure for DNA, heralded a revolution in our understanding of biology at the molecular level. The fact that it.