
How do you draw the graph of y=2sinx for 0
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
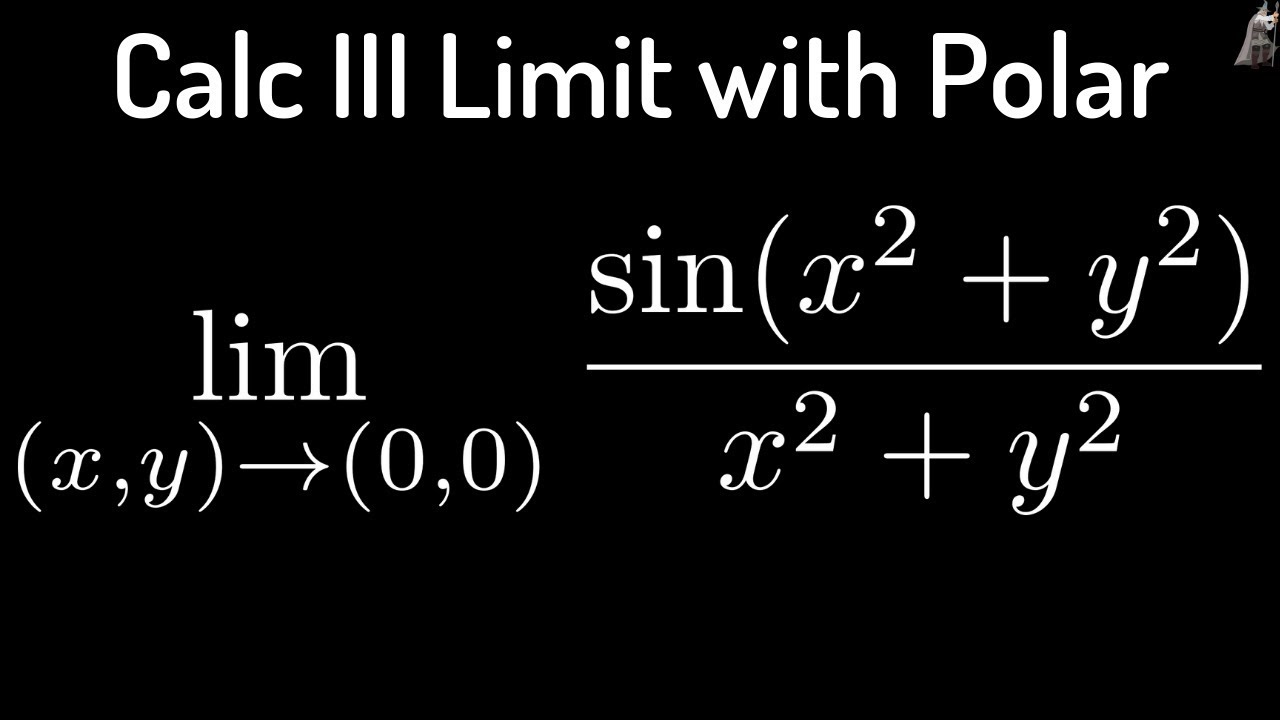
Limit of sin(x^2 + y^2)/(x^2 + y^2) using Polar Coordinates and L'Hopital's Rule YouTube
In Trigonometry Formulas, we will learn. Basic Formulas. sin, cos tan at 0, 30, 45, 60 degrees. Pythagorean Identities. Sign of sin, cos, tan in different quandrants. Radians. Negative angles (Even-Odd Identities) Value of sin, cos, tan repeats after 2π. Shifting angle by π/2, π, 3π/2 (Co-Function Identities or Periodicity Identities)
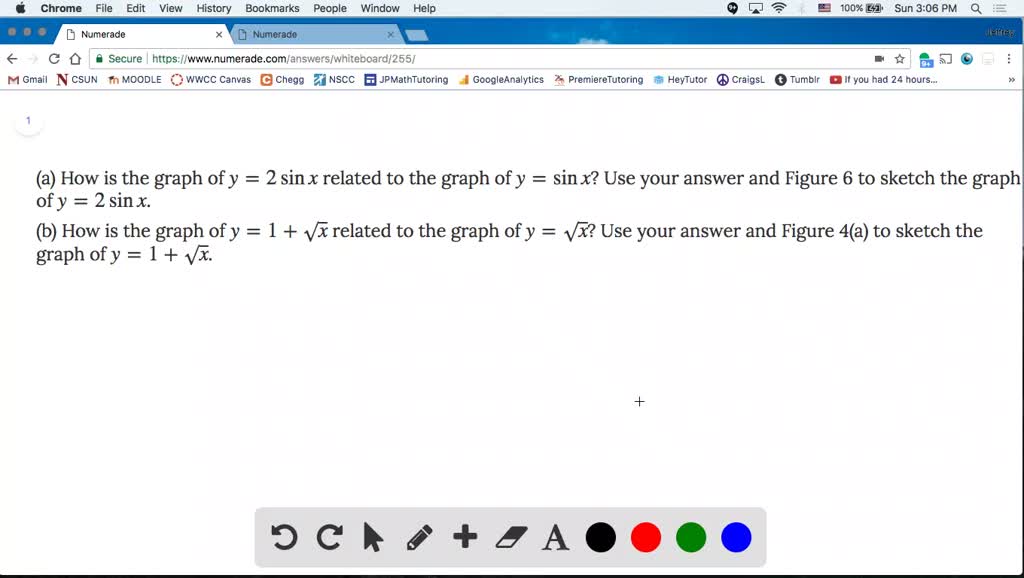
SOLVED(a) How is the graph of y=2 sin x related to the graph of y=sinx ? Use your answer and
Graph y=2sin (x) y = 2sin(x) y = 2 sin ( x) Use the form asin(bx−c)+ d a sin ( b x - c) + d to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift. a = 2 a = 2 b = 1 b = 1 c = 0 c = 0 d = 0 d = 0 Find the amplitude |a| | a |. Amplitude: 2 2 Find the period of 2sin(x) 2 sin ( x). Tap for more steps. 2π 2 π
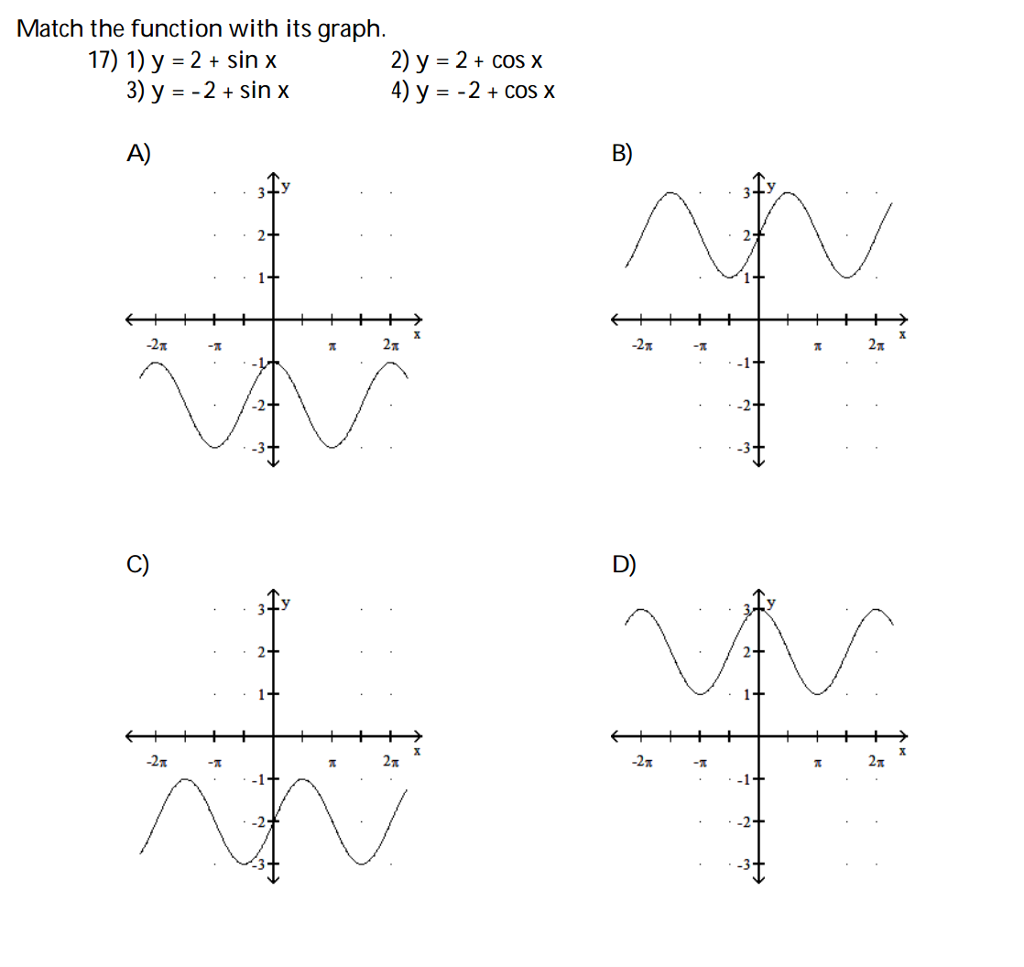
Solved Match the function with its graph. 1) y = 2 + sin x
Popular Problems Trigonometry Graph y=sin (x)^2 y = sin2 (x) y = sin 2 ( x) Graph. y = sin2 (x) y = sin 2 ( x) Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor.

Gambarlah grafik y = 2 sin x ∘ , 0 ≤ x ≤ 36 0 ∘
To shift such a graph vertically, one needs only to change the function to f (x) = sin (x) + c , where c is some constant. Thus the y-coordinate of the graph, which was previously sin (x) , is now sin (x) + 2 . All values of y shift by two. PHASE SHIFT. Phase shift is any change that occurs in the phase of one quantity, or in the phase.

Misc 4 Prove (cos x cos y)2 + (sin x sin y)2 Chapter 3
Quiz Trigonometry y = 2sin(x) Similar Problems from Web Search Finding area of y = tanx and y = 2sinx https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/138217/finding-area-of-y-tan-x-and-y-2-sin-x Edit: Completely rewritten to correct a misreading of the original problem. You know that the graphs of y = tanx and y = 2sinx cross at x= 0.
Презентация "Тригонометрические функции и их графики" скачать бесплатно
integrate x/(x-1) integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1-sqrt(x)) integrate x/(x+1)^3 from 0 to infinity; integrate 1/(cos(x)+2) from 0 to 2pi; integrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi; View more examples; Access instant learning tools. Get immediate feedback and guidance with step-by-step solutions for integrals and Wolfram Problem.
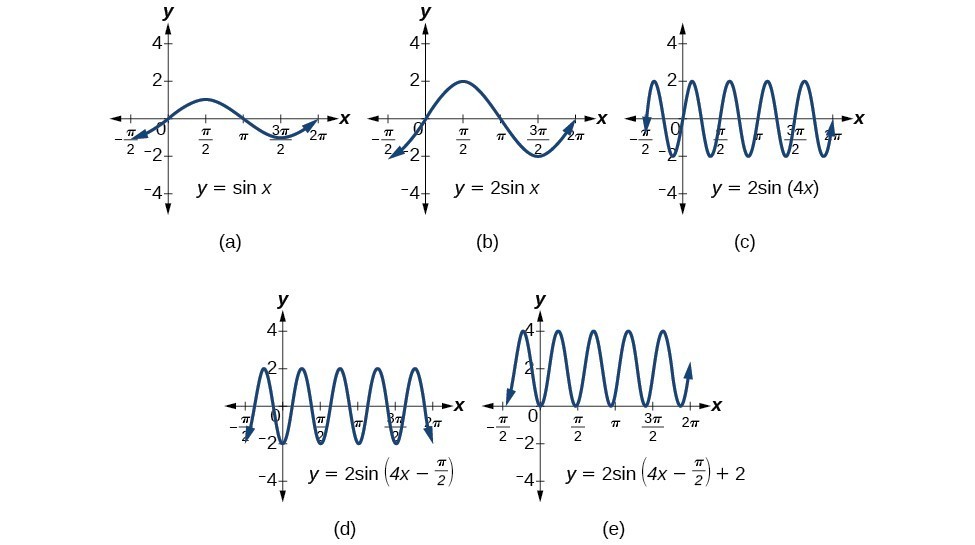
Modeling with Trigonometric Equations Precalculus II
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical.

Solved To obtain the graph of y = 2 + sin (x), we start with
We can find the. How do you find the derivative of y = sin(x + y) ? dxdy = 1−cos(x+y)cos(x+y) Explanation: You simply differentiate both sides with. Hint: The volume generated by the first half of the sine function (over y = 2) is not the same as the volume generated by the second half (below y = 2) because the radii of rotation are not.

Compare the graphs of y=\sin 2 x and y=2 \sin x over the Quizlet
Free trigonometric identity calculator - verify trigonometric identities step-by-step.

Properties of Graphs of Trigonometric Functions ‹ OpenCurriculum
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.
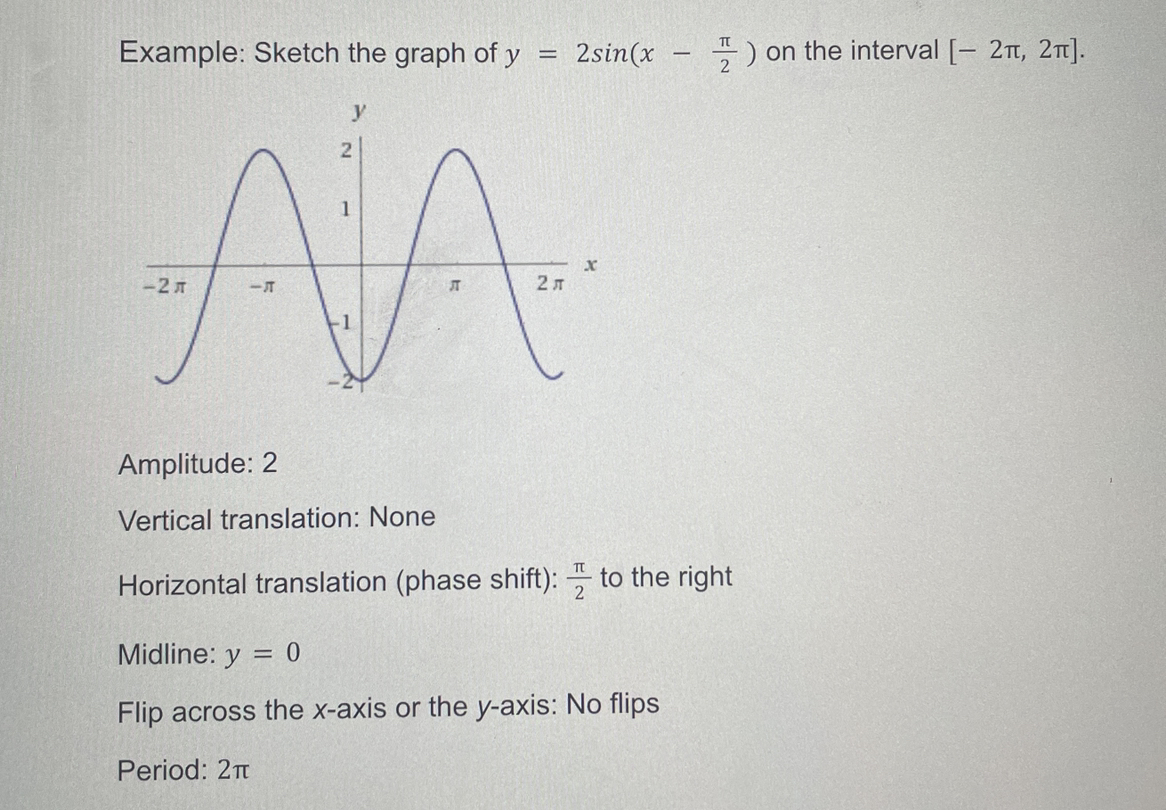
SOLVED Example Sketch the graph of y=2 sin(x(π)/(2)) on the interval [2 π, 2 π]. Amplitude
cos x - cos y = -2 sin( (x - y)/2 ) sin( (x + y)/2 ) Trig Table of Common Angles; angle 0 30 45 60 90; sin ^2 (a) 0/4 : 1/4 : 2/4 : 3/4 : 4/4 : cos ^2 (a) 4/4 : 3/4 : 2/4 : 1/4 : 0/4 : tan ^2 (a) 0/4 : 1/3 : 2/2 : 3/1 : 4/0 ; Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b opposite B, c opposite C:
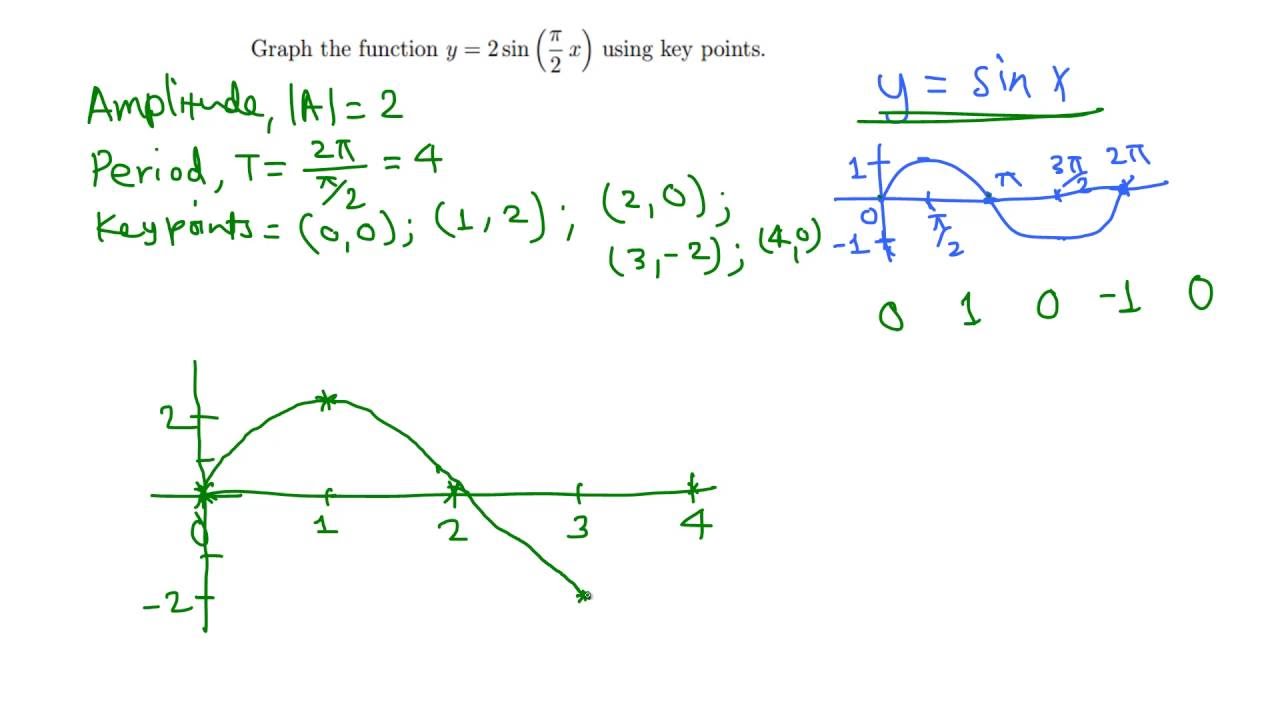
Graph of y = 2 sin( pi/2 x) using key points YouTube
In Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas. These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc. Some formulas including the sign of ratios in different quadrants, involving co-function identities (shifting angles), sum & difference identities, double angle identities.
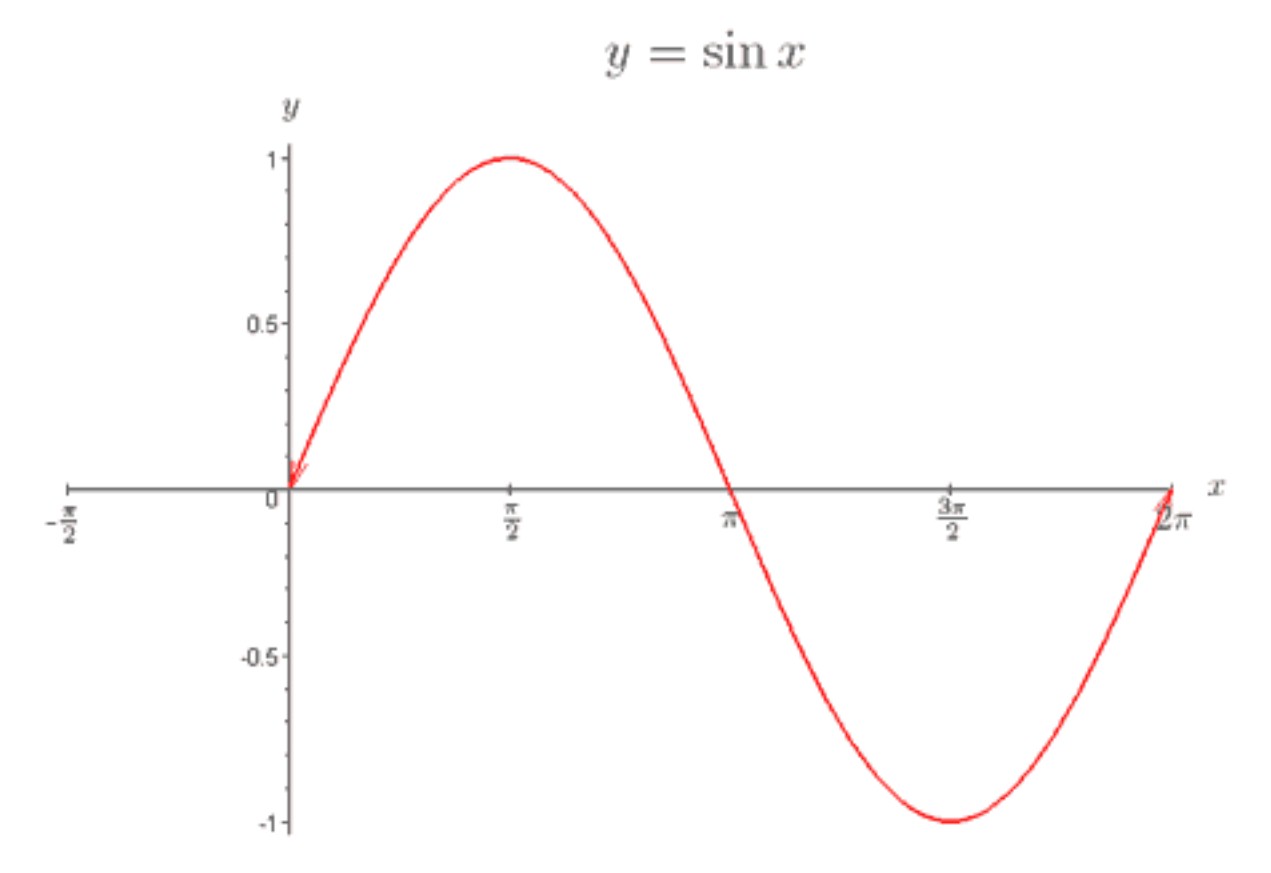
How to Sketch Trigonometric Functions Crystal Clear Mathematics
ordinary differential equations - How to solve $y''' - y = 2\sin (x)$ - Mathematics Stack Exchange How to solve Ask Question Asked 9 years, 10 months ago Modified 9 years, 10 months ago Viewed 3k times 8

Trigonometry graphing the sine, cosine and tangent functions
prove this identity : sin(x + y) sin(x − y) =sin2 x −sin2 y I tried solving it with additional formulas but I can't get the right answer. I get sin2 xcos2 y −cos2 xsin2 y trigonometry Share Cite Follow edited Feb 6, 2014 at 9:26 Paul 19.1k 4 56 80 asked Feb 6, 2014 at 9:24 dona12 183 1 3 11
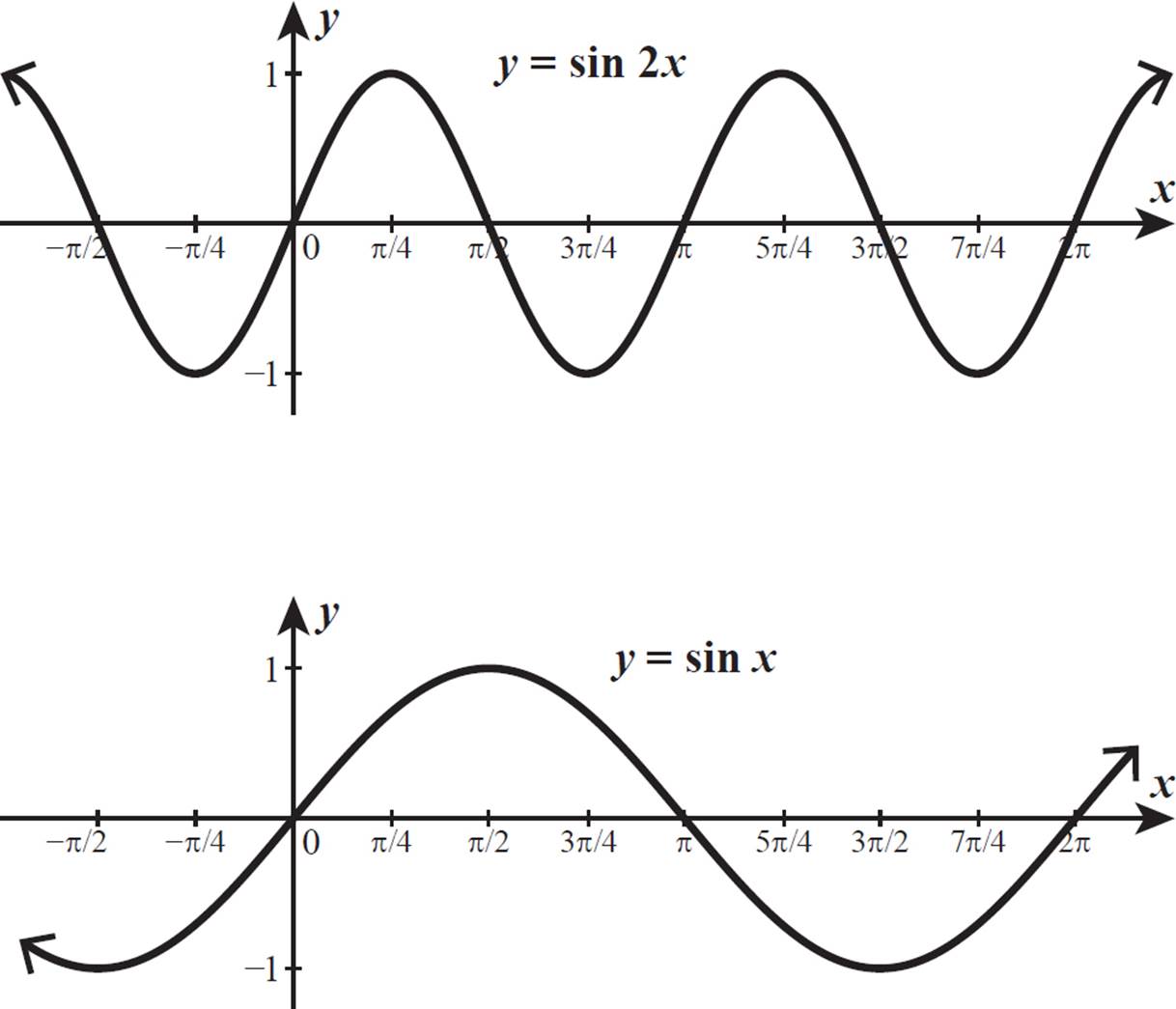
Graphing Trigonometric Functions Trigonometric Functions High School Algebra II Unlocked (2016)
What is a basic trigonometric equation? A basic trigonometric equation has the form sin (x)=a, cos (x)=a, tan (x)=a, cot (x)=a Show more Spinning The Unit Circle (Evaluating Trig Functions ) If you've ever taken a ferris wheel ride then you know about periodic motion, you go up and down over and over. Save to Notebook! Sign in